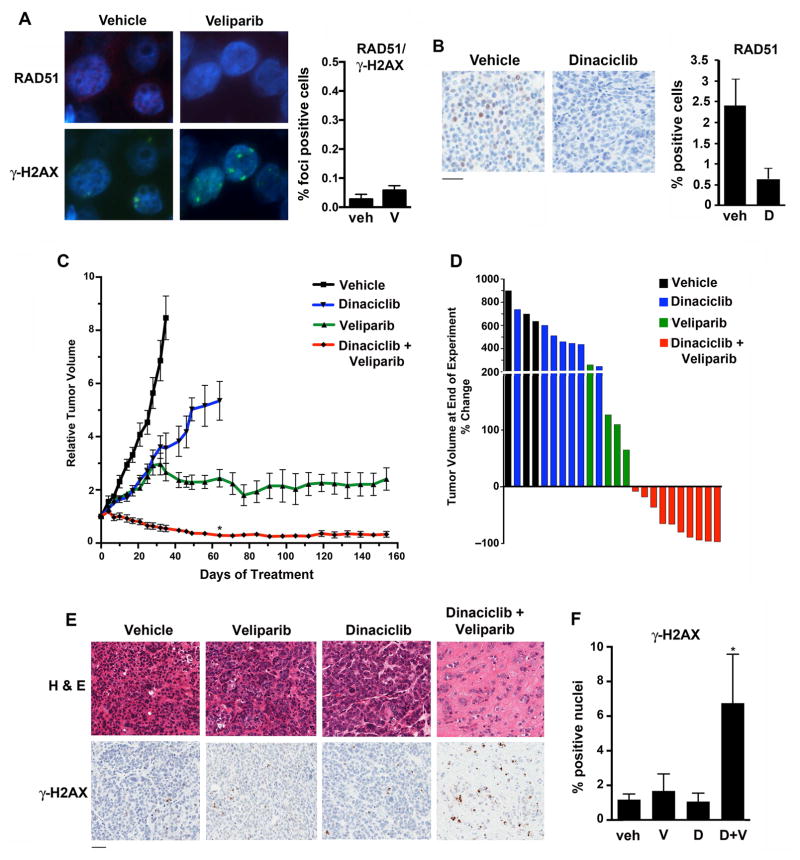
Figure 7. Treatment of the 11–26 PDX model harboring somatic BRCA1 R1443* mutation.
(A) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle or veliparib (n = 5/group). (Left) After 15 days, mice were sacrificed and tumors subjected to immunofluorescence for RAD51 and γ-H2AX foci. (Right) Quantification of γ-H2AX-positive cells with > 5 RAD51 foci. P, non-significant. (B) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle or dinaciclib for 2 doses over 5 days (n = 3/group), after which mice were sacrificed and tumors stained for RAD51. P = 0.059. Bar, 100 μm. (C) Mice bearing xenografts were treated with vehicle (n = 3), dinaciclib (n = 7), veliparib (n = 4) or the combination (n = 10), demonstrating long-term growth control with veliparib and sustained tumor regressions with combination treatment. After 2 months of treatment (day 61), P < 0.001 (*) for combination treatment vs. either monotherapy. (D) Waterfall plot demonstrating % change in tumor volume at the time of sacrifice for individual mice in the four treatment groups. (E) Representative end-of-experiment histology (H & E) and γ-H2AX staining of tumors isolated from mice in the 4 treatment groups. Bar, 100 μm. (F) Quantification of % nuclei staining positively for γ-H2AX at end-of-experiment (* P < 0.05 for combination vs. control treatment).