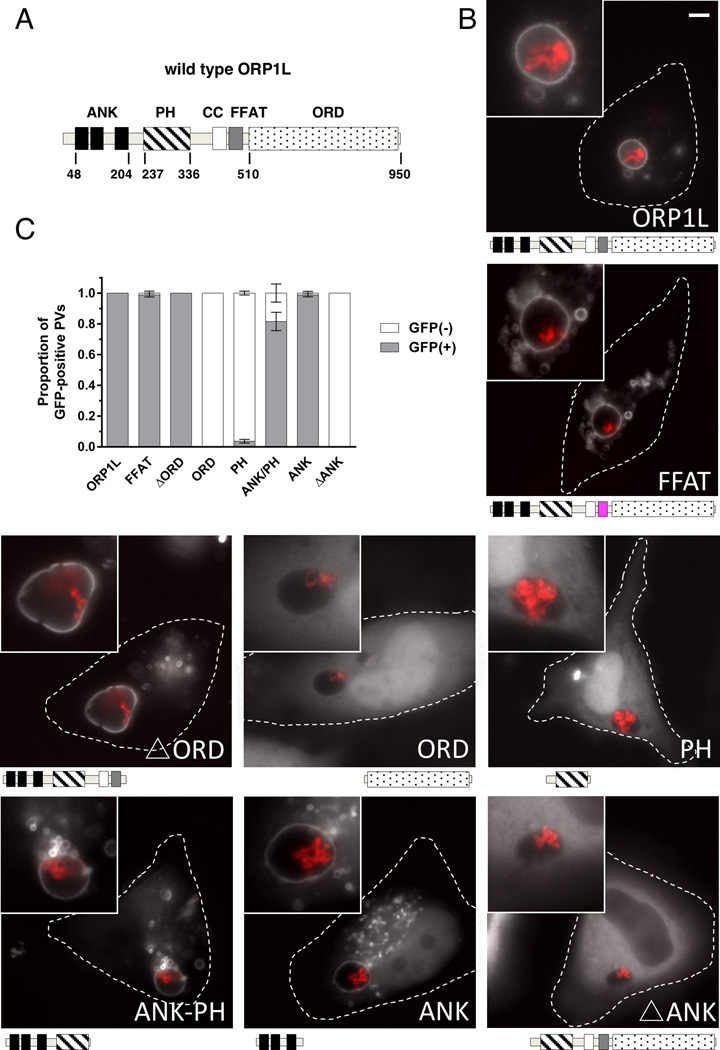
Figure 3. The ankryin repeat domains are necessary and sufficient to target ORP1L to the PV.
(A) Stick diagram of ORP1L protein domains. ANK = ankryin repeats (black), PH = plekstrin homology domain (stripe), CC = coiled-coil domain (white), FFAT = two phenylalanines in an acidic tract (gray), ORD = OSBP-related ligand binding domain (dots). Numbers represents amino acid position. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with C-terminal GFP constructs and infected with mCherry-expressing C. burnetii. Domain constructs are represented below each image. At 3 days post infection, live cells were imaged by wide field fluorescence microscopy. FFAT mutant (D478A) (magenta), Ank-PH, and Ank localize to the PV membrane, while ORD, Δ Ank, and PH remain cytoplasmic without PV membrane localization. Green = ORP1L-GFP, Red = mCherry-C. burnetii. Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) Quantitation of PV localization of ORP1L domain constructs. Shown are the results from two independent experiments, with at least 30 PVs per condition per experiment. Error bars represent SEM.