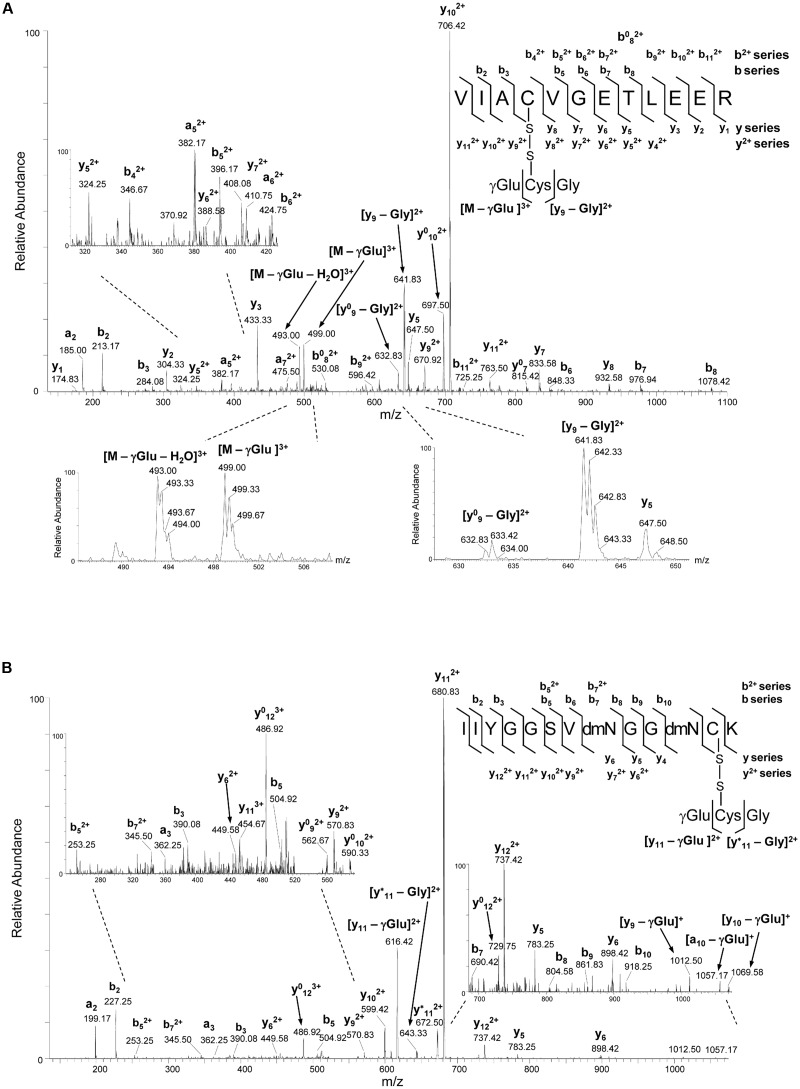
FIGURE 5.
NanoLC-MS/MS analysis of cTPI tryptic peptides modified by GSSG. (A) CID MS/MS fragmentation spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z of 542.573+ corresponding to S-glutathionylated peptide with the sequence 124VIACVGETLEER135. The detection of ion at m/z 499.00 indicate the loss of γGlu (-129 Da) from the triply charged precursor resulting in the ion [M – γGlu]3+, while the concomitant loss of water (-18 Da) resulted in the ion at m/z 493.00 corresponding to [M – γGlu – H2O]3+. Sequence specific y- and b-type fragment ion signals of different charge states (+1 and +2) identifying the peptide, and metastable decomposition product ions resulting from further internal fragmentation of glutathione adduct by elimination of γGlu or Gly residues are indicated. The peaks denoted y0 and b0 are the result of water (-18 Da) loss from corresponding ion. Spectral portions containing signature ions resulting from the loss of γGlu or Gly residues in glutathione with partly isotopically resolved peaks indicating ions charge state are shown. (B) CID MS/MS fragmentation spectrum of the precursor ion at m/z of 530.213+ corresponding to S-glutathionylated peptide with the sequence 207IIYGGSVNGGNCK219. The expanded regions of the product ion spectra showing detailed fragmentation pathways of S-glutathionylated peptides are given on the left side of panel (A) and on both left and right sides of panel (B). Product maps indicating the cleavage sites in CID MS/MS are given on the right side of panels (A,B).