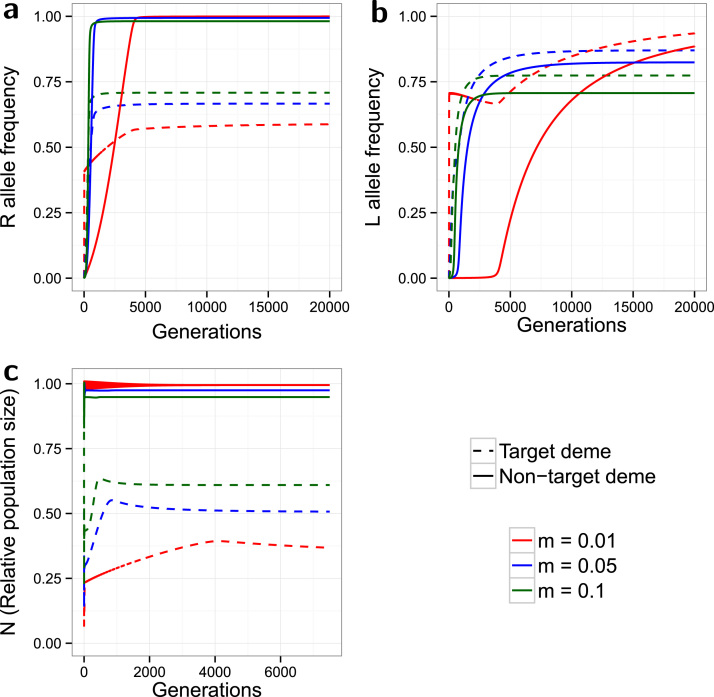
Fig. 7.
Less dominant, complete, no-cost resistance. Evolution of the R allele frequency (a), the L allele frequency (b), and the change in the relative population size over time (c). The model is spatial, with release ratio d=20, and a partially dominant complete resistance (, ) with no associated costs (). Dashed lines indicate the target deme, solid lines indicate the non-target deme, and the line colours indicate the simulated dispersal rate (see legend). Note the longer time scale (20,000 generations) than that shown in earlier figures. Only 7500 generations are shown for (c) to highlight the local peak in the target population size. The near fixation of resistance in the non-target deme drives an increase in the frequency of the lethal construct in that deme. Through migration, this increases the L allele frequency in the target deme also, which ultimately increases the effectiveness of target population control.