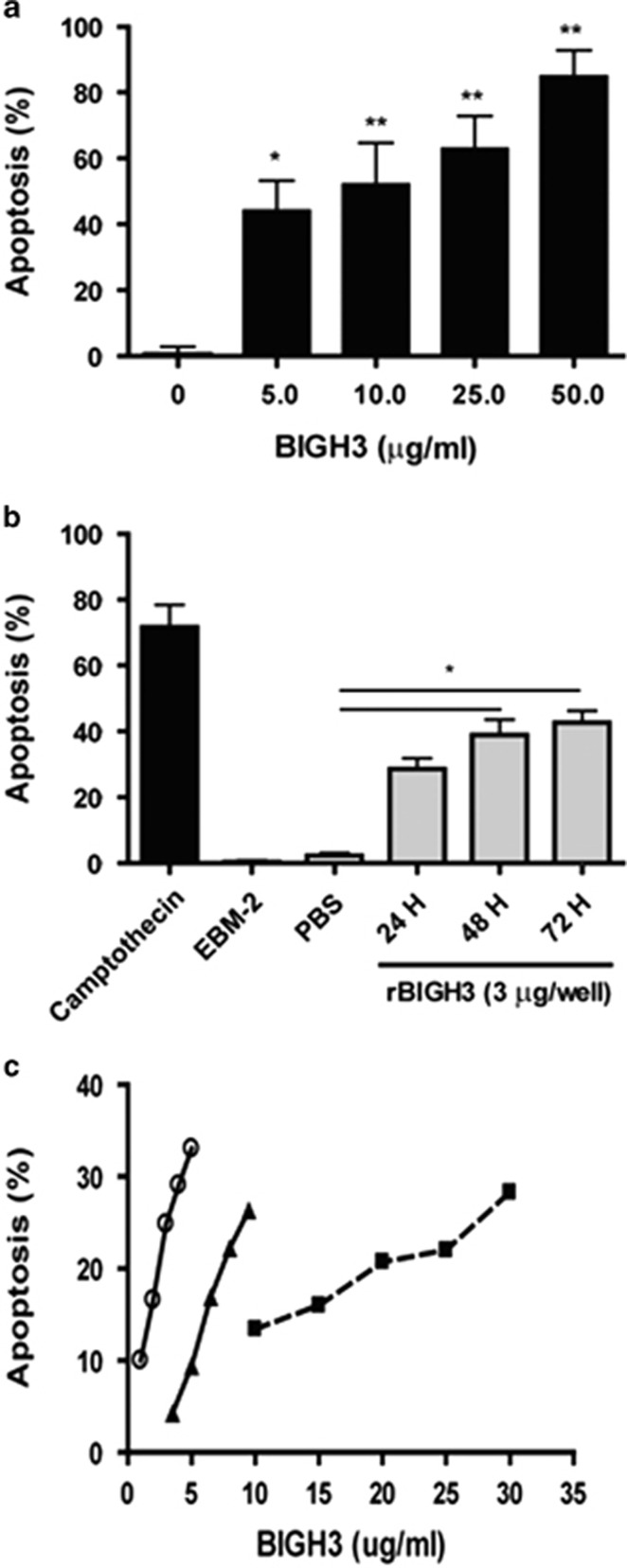
Figure 4.
BIGH3 induced HRP apoptosis. (a) Dose-dependent increase in apoptosis: HRP were cultured in media containing recombinant BIGH3 protein at increasing concentrations. TUNEL assay was performed following 24 h treatment period, and a dose-dependent relationship existed between BIGH3 amount and percent apoptosis. Results from one-way ANOVA were significant (F(4,18)=9.154; P<0.001). A Dunnett's multiple comparison test was performed using 0 μg/ml as the control (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). (b) Time-dependent increase in apoptosis: cultured HRP were treated with 3 μg/ml of BIGH3 protein for 72 h. TUNEL assay was performed every 24 h, and a time-dependent relationship was observed. One-way ANOVA was significant (F(5,11)=17.54; P<0.01) and Dunnett's test was performed using recombinant BIGH3 vehicle (PBS) as control (*P<0.05). Camptothecin used a positive control (72 h; topoisomerase I inhibitor). (c) Cell type dependency in apoptosis: HRP (open circle), rhesus monkey RECs (closed triangle) and human RPTECs (closed square) were cultured and treated with increasing concentrations of BIGH3 protein. Cell Death was confirmed by TUNEL assay following 24 h treatment period. HRP were most sensitive to low concentration (1–5 μg/ml) of BIGH3 treatment which induced a 25% increase in apoptosis (or 6% increase in apoptosis per unit increase in BIGH3 concentration—μg/ml). RhRECs were less sensitive to BIGH3 treatment (2–10 μg/ml) which induced a 22% increase in cell apoptosis (or 2.5% increase in apoptosis per unit increase in BIGH3 concentration—μg/ml). RPTEC were the least sensitive to BIGH3 treatment (at a higher concentration of 10–30 μg/ml) which induced a 16% increase in cell apoptosis (or 0.8% increase in apoptosis per unit increase in BIGH3 concentration—μg/ml).