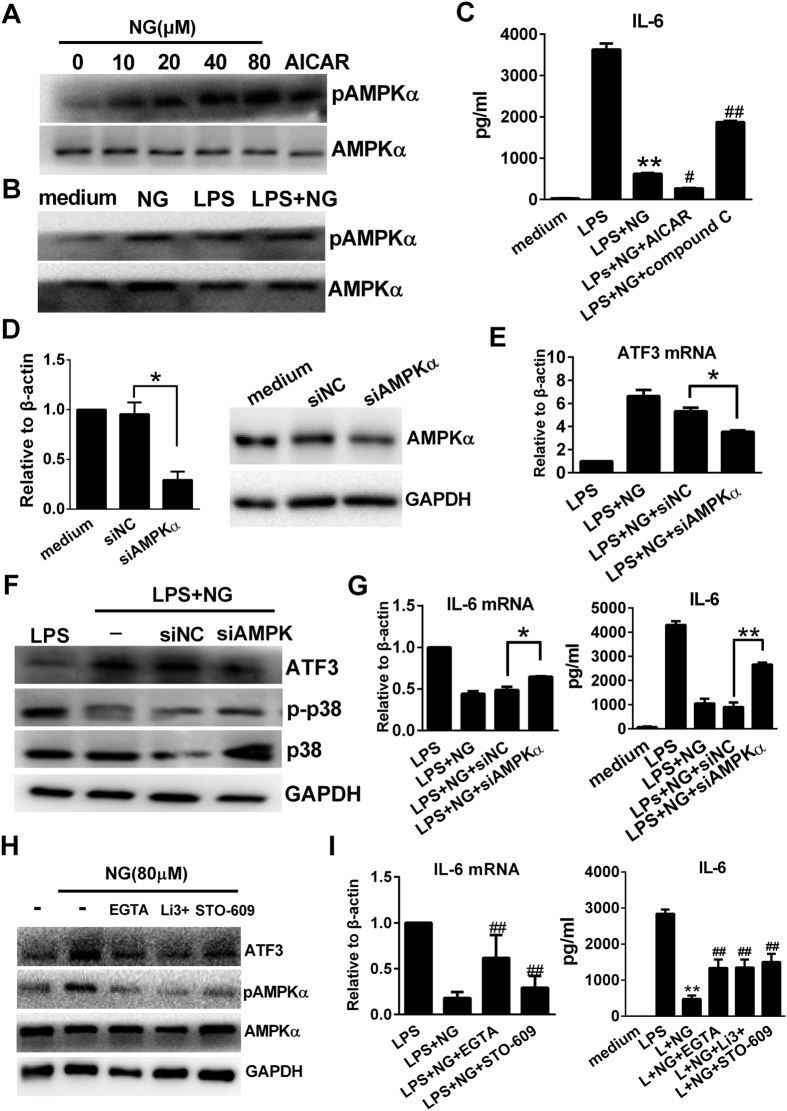
Figure 5. Naringenin activates AMPKα to mediate ATF3 upregulation in RAW 264.7 cells.
(A) Dose-dependent induction of AMPK phosphorylation by naringenin. Cells were treated with NG (0, 10, 20, 40 and 80 μM) or 1 mM AICAR for 1 h. The phosphorylation of AMPKα was detected by western blot. (B) Naringenin enhances AMPK phosphorylation with LPS. Cells were treated with NG, LPS or LPS plus NG for 1 h. AMPKα phosphorylation was detected by western blot. (C) Modulation of AMPK affects IL-6 suppression by naringenin. Cells were treated with NG alone or in combination with 1 mM AICAR or 2 μM compound C before stimulation with LPS. Supernatant IL-6 was detected by ELISA (n = 3). **P < 0.01 vs LPS; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs LPS + NG (D) AMPK knockdown by siRNA. Cells were transfected with control siRNA (siNC) or AMPKα siRNA (siAMPKα) for 24 h. Then, AMPKα mRNA was detected by PCR (n = 3, *P < 0.05). The protein level of ATF3 was detected by western blot. Uncropped images are presented in Supplementary Figure S8B. (E–G) ATF3 expression and anti-inflammatory activity affected by AMPKα siRNA. Wild-type cells and siNC- or siAMPKα-transfected cells were treated with LPS alone or LPS plus NG. The mRNA expression of ATF3 was detected by RT-PCR (E) (n = 3, *P < 0.05). Then, ATF3, p-p38, p38 and tubulin were detected by western blot (F). The mRNA and protein levels of IL-6 were detected by RT-PCR and ELISA (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (H–I) Effects of calcium and CaMKKβ inhibition on cytokine production and ATF3/AMPKα activation. Cells were pretreated with 5 mM EGTA, 10 μM LiCl3 (Li3+) or 1 μM STO-609 before treating with NG alone or in combination with LPS. mRNA expression of IL-6 was detected by RT-PCR. The supernatant level of IL-6 was detected by ELISA n=3, **P < 0.01 vs LPS, ##P < 0.01 vs LPS + NG. ATF3, p-AMPK, AMPK and GAPDH were detected by western blot. Uncropped images are presented in Supplementary Figure S8B. Naringenin is abbreviated as NG. The concentrations of LPS and NG were 100 ng/ml and 80 μM unless indicated.