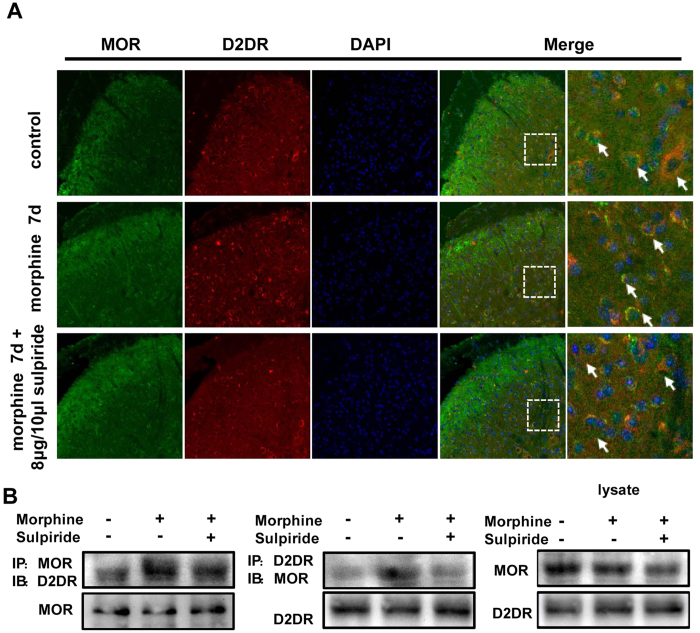
Figure 6. Chronic morphine treatment increases the MOR/D2DR interactions in the spinal cord dorsal horn and spinal D2DR inhibition with D2DR antagonist disrupts these interactions.
(A) Double immunofluorescence staining showed that MOR (green) and D2DR (red) were co-localized in the mice spinal cord (20X magnification). Chronic morphine treatment increased the co-localization of MOR and D2DR in the spinal cord, and D2DR antagonist sulpiride (8 μg/10 μl, i.t.) reduced the increased co-expression of D2DR with MOR (n = 4). (B) Co-IP experiments showed that D2DR could interact with MOR, and the MOR/D2DR interactions were increased in the spinal dorsal horn after chronic morphine treatment for 7 days while D2DR antagonist sulpiride (8 μg/10 μl, i.t.) disrupted the interactions of the MOR/D2DR (n = 3).