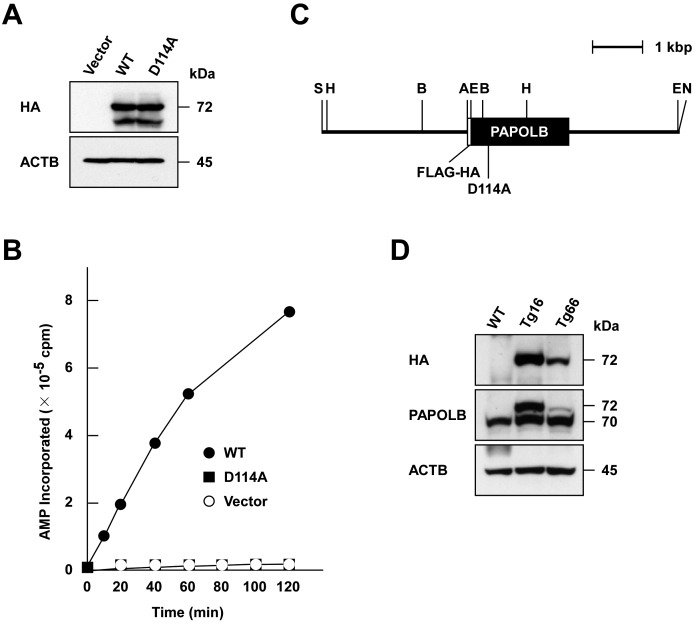
Fig. 2.
Generation of transgenic mice expressing polyadenylation-defective PAPOLBD114A. (A) Immunoblot analysis of proteins synthesized in vitro. N-terminally FLAG- and HA-tagged PAPOLB (WT) and PAPOLBD114A (D114A) were synthesized in rabbit reticulocyte lysates and were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA antibody. ACTB was used as a control. (B) Polyadenylation assay. The polyadenylation activity of wild-type PAPOLB (closed circle) and PAPOLBD114A (closed square) was monitored by measuring the incorporation of AMP from [α-32P]ATP into an oligo(A)12 primer at the incubation times indicated. Empty vector (open circle) was used as a control. (C) Physical map of the transgenic construct. The protein-coding regions of FLAG and HA tags and PAPOLBD114A are indicated by open and filled boxes, respectively. The restriction enzymes are denoted as follows: A, ApaI; B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; S, SalI; N, NotI. (D) Immunoblot analysis. Testicular protein extracts of wild-type (WT) and two transgenic mouse lines (Tg16 and Tg66) were probed with anti-HA and anti-PAPOLB antibodies. ACTB served as a control.