Fig. 4.
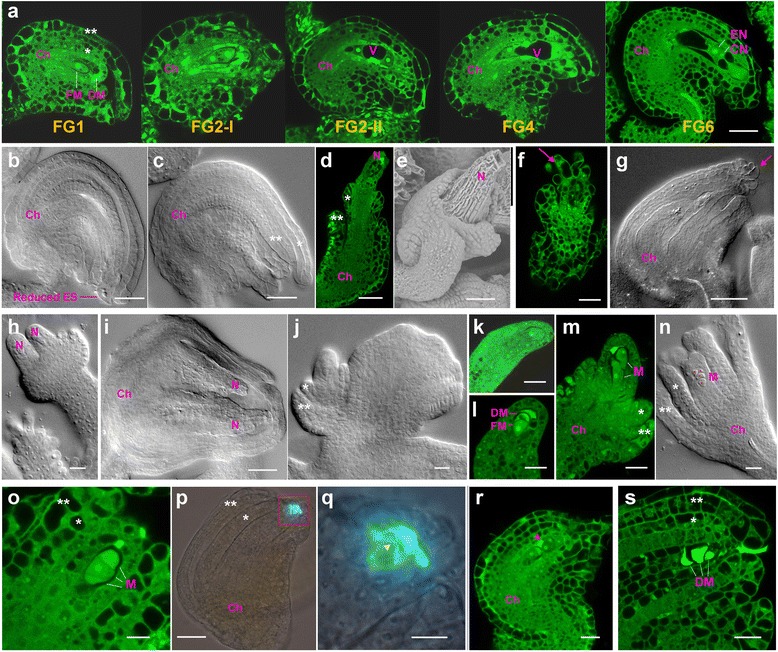
Phenotypic analysis of atring1a;atring1b during ovule and ES development. a. Ovule and ES development stages in WT. Functional (FM) and degenerated megaspores (DM) are showed at FG1 stage. Strong autofluorescence indicates DM. A two-nucleate ES is shown in early FG2 (FG2-I); an enlarged central vacuole and a small chalazal vacuole appear in the late FG2 (FG2-II). A four-nucleate ES develops at FG4. A mature seven-celled ES is produced at FG6. (ES stages are defined according to [7].) b–s Ovule and ES development in the atring1a;atring1b strong mutants. b Reduced ES and mildly proliferated nucellus in a mature ovule. c No obvious ES development. d, e Arrested outer integument and overproliferated nucellus. f Young mutant ovule with stigmatic papilla-like structure arising from nucellar epidermis. g Ovule-to-carpel conversion. h, i Double nucelli in one ovule. j Outer integument develops into leaf-like structure. k A normally differentiated MMC at stage FG0. l Developing ovule primordium at stage FG1 without integument initiation. m Developing ovule primordium with two surviving megaspores but severely inhibited integument growth. n All four surviving megaspores become arrested at later stage. o Three arrested megaspores at later stage. p Aniline blue staining showing growth arrest of two megaspores in a mature ovule. Callose accumulation indicated by bright cyan. q Close-up view of p. Yellow arrowhead indicates cell plate. r One of several megaspores can occasionally undergo one mitotic division to enter into FG2 stage (arrowhead). s Arrested megaspores gradually undergo degeneration during later development. * inner integument, ** outer integument, Ch chalazal, CN central cell nucleus, DM degenerated megaspore, EN egg cell nucleus, FM functional megaspore, M megaspore, N nucellus, V large vacuole. Bars = 10 μm, except 50 μm in a–e, g, i, and p
