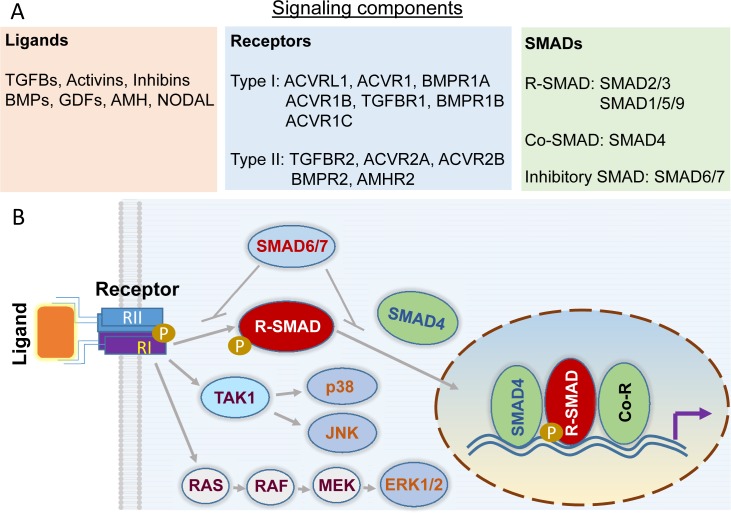
FIG. 1.
TGFB signal transduction. A) Core elements of canonical TGFB superfamily signaling. The major ligands, type II and type I receptors, and SMADs are listed. To our knowledge, mRNA and/or protein expression of all listed signaling elements except ACVRL1 and ACVR1C has been reported in human GCT and/or GCT cell lines (i.e., KGN and COV434). B) The TGFB signaling paradigm. TGFB signal transduction is initiated by ligand-receptor binding and propagated through intracellular SMAD proteins. Phosphorylated R-SMADs interact with SMAD4, resulting in nuclear accumulation of the R-SMADs-SMAD4 complex that regulates gene transcription together with coregulators (Co-R) consisting of co-activators and corepressors. SMAD6/7 acts as negative modulators of TGFB signaling activity. Besides the canonical SMAD-dependent signaling, TGFB signaling is also mediated via non-SMAD pathways. SMAD-independent activation of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK is illustrated as examples. This is a simplified illustration of TGFB signaling with the purpose of highlighting major signaling elements.