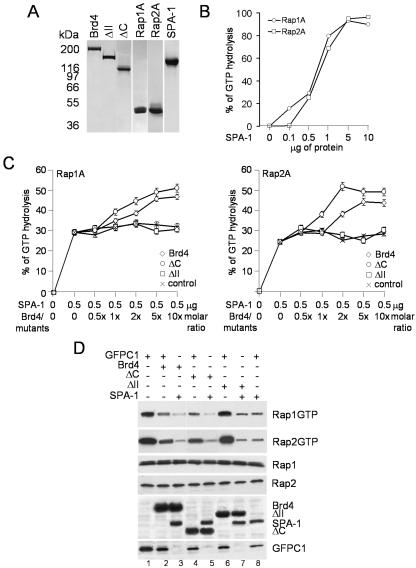
FIG. 4.
Effects of Brd4 on Rap GAP activity of SPA-1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) Coomassie blue staining of recombinant proteins. Purified recombinant SPA-1, Brd4, ΔC, and ΔII, as well as Rap1A and Rap2A, were electrophoresed in a 4 to 20% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel and used for the in vitro assay. (B) GAP activity of SPA-1 on Rap1A and Rap2A. SPA-1 activity was measured by incubating 3 μg of Rap 1A or Rap2A with indicated amounts of SPA-1 as described under Materials and Methods. (C) SPA-1 GAP activity assayed in the presence of Brd4 or Brd4 deletion mutants. Increasing molar ratios of Brd4 or Brd4 mutants were incubated with 0.5 μg of SPA-1. Control represents SPA-1 activity on Rap1A or Rap2A in the presence of bovine serum albumin. Values represent the averages from three independent experiments. (D) Rap activation assay in NIH 3T3 cells. NIH 3T3 cells (1.6 × 106) were transfected with 2 μg of pEGFP-SPA-1 alone (lane 8) or together with 2 μg of pEGFP-Brd4 (lane 3) or pEGFP-Brd4 deletion mutants (lanes 5 and 7), with the total amount of plasmids being adjusted to 4 μg with control plasmid pEGFP-C1. Lysates were precipitated with GST-RalGDS-RBD or control GST, and bound materials were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to Rap1 and Rap2. Brd4, Brd4 deletion mutants, and SPA-1 in lysates were detected by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody.