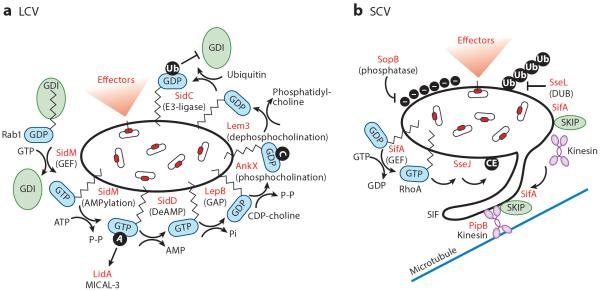
Figure 4.
Effector-mediated remodeling of pathogen-containing vacuoles: Legionella-containing vacuoles (LCV) and Salmonella-containing vacuoles (SCV). (a) Legionella encodes multiple effectors that regulate Rab1 activity. SidM is a multidomain effector with both Rab1 GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor) activity and AMPylation activity (black circle labeled A). SidD can deAMPylate Rab1. Rab1 can be inactivated by the GAP (GTPase-activating protein) LepB. Furthermore, Rab1 can be modified by the addition of phosphocholine by AnkX through its FIC (filamentation induced by cAMP) domain (black circle labeled C) or by the removal of the phosphocholine by Lem3. Lastly, the ubiquitin ligase SidC is thought to ubiquitinate (black circle labeled Ub) Rab1, preventing its interaction with its GDI (guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor). (b) Salmonella modifies its SCV through the action of multiple effectors. The SPI-1-secreted effector SopB, a phosphoinositide phosphatase, is involved in invasion and alters the surface charge (black circles labeled with minus signs) of the SCV to prevent lysosomal fusion. SifA is a key effector regulating SCV maintenance and Salmonella-induced filament (SIF) formation. SifA, a SPI-2 effector, interacts with the host protein SKIP (SifA kinesin-interacting protein) to retain SCV perinuclear positioning through kinesin and PipB2 interactions. In addition, the GEF domain of SifA is thought to activate RhoA GTPase at the SCV, which subsequently induces the acyltransferase activity of the SPI-2 effector SseJ, generating cholesterol esters on the SCV (black circle labeled CE). These events are thought to promote SIF formation. SseL, through its deubiquitinase (DUB) activity, reverses SCV ubiquitination and host cell recognition by autophagosomes.