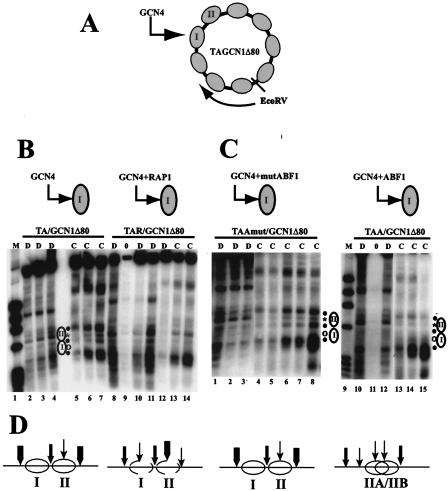
FIG. 1.
ABF1 perturbs nucleosome positioning via a nucleosomal binding site similarly to RAP1. (A) Schematic diagram of plasmid TA/GCN1Δ80. The gray ellipses represent positioned nucleosomes, and nucleosomes I and II are marked. Nucleosome I contains the GCN4 binding site, as shown, and chromatin structure was mapped clockwise from the EcoRV site, as indicated, by use of chromatin prepared from FY24 yeast cells containing the indicated plasmid episome. (B) Indirect end-label analysis of TA/GCN1Δ80 and TAR/GCN1Δ80 chromatin structure. TAR/GCN1Δ80 is similar to TA/GCN1Δ80 except for a RAP1 binding site introduced adjacent to the GCN4 binding site. MNase cleavage sites were mapped clockwise from the EcoRV site in naked DNA (D lanes) or in chromatin (C lanes) from cells grown in glucose medium under conditions that are noninducing for Gcn4p activation. Lane 1 contains φX/HaeIII marker DNA. Naked DNA in TA/GCN1Δ80 (lanes 2 to 4) and in TAR/GCN1Δ80 (lanes 8, 10, and 11) was digested using 2.5 (lanes 2 and 8), 5 (lanes 3 and 10), or 10 (lane 4 and 11) U of MNase per ml. Chromatin was digested using 0 (lane 9), 2.5 (lanes 5 and 12), 5 (lanes 6 and 13), or 10 (lanes 7 and 14) U/ml. (C) Indirect end-label analysis of TAA/GCN1Δ80 and TAAmut/GCN1Δ80 chromatin structure. TAA/GCN1Δ80 and TAAmut/GCN1Δ80 are similar to TA/GCN1Δ80, except for ABF1 or mutated ABF1 binding sites introduced adjacent to the GCN4 binding site. MNase cleavage sites were mapped clockwise from the EcoRV site in naked DNA (D lanes) or in chromatin (C lanes) from cells grown in glucose medium. Lane 9 contains φX/HaeIII marker DNA. Naked TAA/GCN1Δ80 and TAAmut/GCN1Δ80 DNA were digested using 2.5 (lanes 1 and 10), 5 (lanes 2 and 12), or 10 (lane 3) U/ml. Chromatin was digested using 0 (lane 11), 2.5 (lanes 4 and 13), 5 (lanes 5 and 14), 10 (lanes 6 and 15), 15 (lane 7), or 20 (lane 8) U of MNase per ml. All the chromatin samples were run on the same gel; the DNA lanes are derived from separate gels (Fig. 3 shows examples in which chromatin and naked DNA samples all derive from the same gel). The asterisks and open circles indicate cleavages in naked DNA that are protected by nucleosomes I and II in chromatin, and filled circles indicate the edges of nucleosomes I and II, which are present in TA/GCN1Δ80 and TAAmut/GCN1Δ80 but not in TAR/GCN1Δ80 and TAA/GCN1Δ80. The locations of positioned nucleosomes I and II are shown by ellipses. (D) Schematic diagram of nucleosome positioning in the region of nucleosomes I and II deduced from the MNase cutting patterns of TA/GCN1Δ80, TAR/GCN1Δ80, TAA/GCN1Δ80, and TAAmut/GCN1Δ80. The thickness of each vertical arrow indicates the relative strength of MNase cleavage.