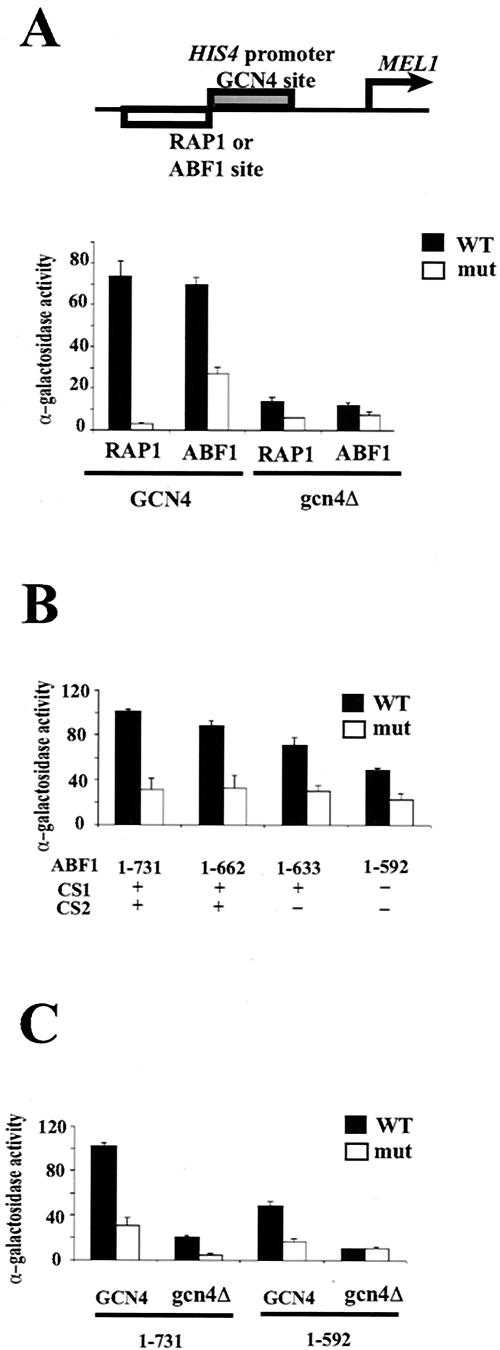
FIG. 4.
ABF1 can contribute to activation of the HIS4 promoter similarly to RAP1. (A) The MEL1 reporter gene fused to modified HIS4 promoter having an ABF1 or RAP1 binding site or mutant ABF1 or RAP1 binding sites adjacent to the GCN4 binding site, schematized at the top. MEL1 activity was monitored in GCN4+ cells or gcn4Δ cells and expressed as α-galactosidase activity. (B) Contribution of C-terminal domains to GCN4-mediated activation of the HIS4 promoter. The modified HIS4 promoter having an ABF1 binding site or mutant ABF1 binding site adjacent to the GCN4 binding site was introduced into yeast expressing ABF1 deletion mutants as indicated, and MEL1 activity was monitored. (C) MEL1 activity was monitored from the modified HIS4 promoter having an ABF1 binding site or mutant ABF1 binding site adjacent to the GCN4 binding site in GCN4+ or gcn4Δ yeast harboring full-length ABF1 (“1-731”) or truncated ABF1 lacking the CS1 and CS2 domains (“1-592”), as indicated. Standard deviations are indicated. WT, wild type.