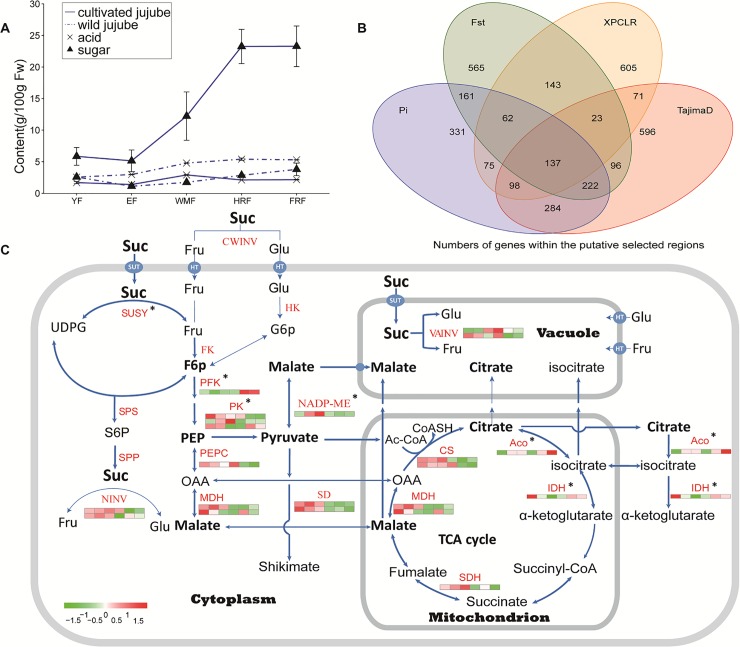
Fig 3. Jujube sugar and acid metabolism associated with domestication.
(A) Sugar and acid accumulation in fruits at various developmental stages from cultivated and wild jujubes. YF, young fruit; EF, expanding fruit; WMF, white mature fruit; HRF, half-red fruit; and FRF, full-red fruit. (B) Number of genes detected in the putative selective regions using different methods. (C) Transcript abundance of genes involved in sugar and acid metabolism in cultivated and wild jujubes. Stars indicate the genes that were located in the regions putatively detected as selective sweeps. Scaled log2 expression values (RPKM) are shown in the heat map legend. The six boxes in one row of each heat map (left to right) correspond to the expression levels at stages EF, HRF and FRF of the wild accession (‘Qingjiansuanzao’) and WMF, HRF and FRF of the ‘Junzao’ cultivar. Each row in the heat map corresponds to one gene. SUSY: sucrose synthase; SPS: sucrose phosphate synthase; SPP: sucrose-phosphatase; HK: hexokinase; FK: fructokinase; PK: pyruvate kinase; MDH: malate dehydrogenase; ACO: aconitate hydratase; IDH: isocitrate dehydrogenase; SDH: succinate dehydrogenase; CS: citrate synthesis; NINV: neutral invertase; CWINV: cell wall invertase; vAINV: vacuolar acid invertase; PFK: 6-phosphofructokinase.