Fig. 2. CLIP-170 and mDia1 form a barbed-end tracking complex that accelerates actin filament elongation.
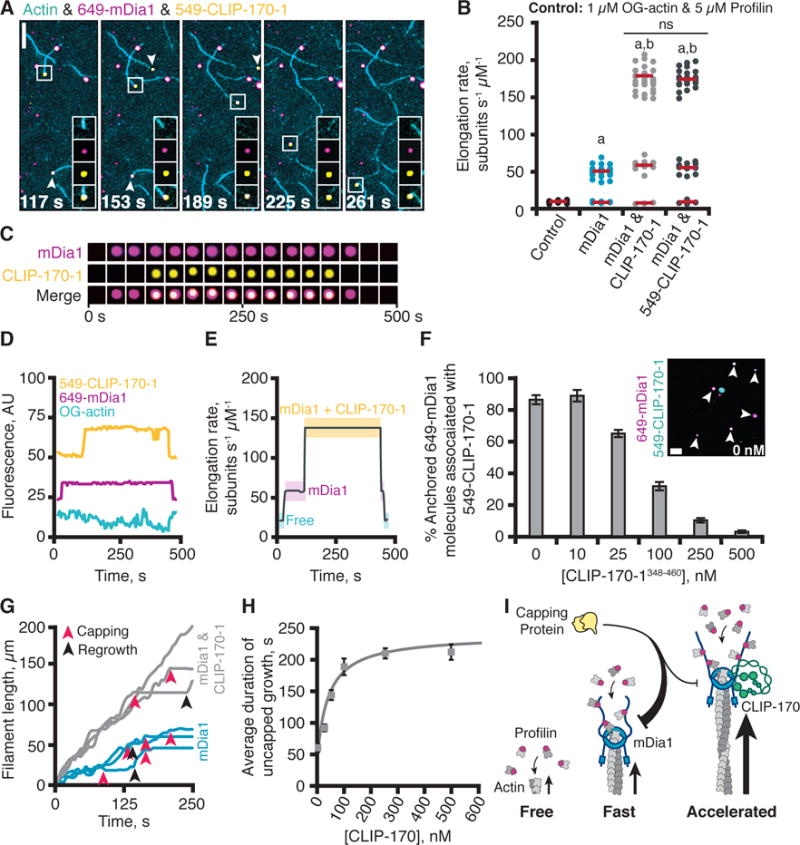
(A) Representative time points from a single molecule TIRF experiment. Reactions contain 1 μM G-actin (10% OG-labeled; 0.2% biotin-actin), 50 pM 649-mDia1, and 25 nM 549-CLIP-170-1. A barbed-end is highlighted in each frame (boxed), with insets showing individual and merged channels. Arrows show two additional growing barbed-ends with 649-mDia1 and 549-CLIP-170-1 associated. Scale bar, 10 μm. Insets 5 × 5 μm. (B) Effects of 25 nM CLIP-170-1 or 549-CLIP-170-1 on rate of mDia1-mediated actin filament elongation. Reactions as in (A). Statistical differences: ns, not significantly different from control; a, compared to control (actin and profilin) (p < 0.05); b, compared to formin control (actin, profilin, and formin) (p < 0.05). (C) Formation and dissociation of a CLIP-170-mDia1 complex at a barbed-end. (D) Fluorescence intensity profiles for each channel showing formation and dissociation of the CLIP-170-mDia1 complex in (C). (E) Elongation rates correlate with arrival and dissociation of mDia1 and/or CLIP-170 at the barbed-end. (F) Single-molecule colocalization of anchored 649-mDia1 and soluble full-length 549-CLIP-170-1 at different concentrations of unlabeled competitor fragment CLIP-170-1348–460. Data averaged from 3 fields of view in each of 3 independent experiments. Error bars, SE. Inset shows a representative field of view from a reaction with no competitor. Scale bar, 5 μm. (G) Representative filament traces from TIRF movies, conditions as in (A) except for the addition of 3 nM CP. Capping events (red arrows) and regrowth events (black arrows) are highlighted. (H) CLIP-170-1 enhances the duration of mDia1-mediated elongation in the presence of CP. Error bars, SE. (I) Cartoon of CLIP-170 joining mDia1 at barbed-end and increasing rate of elongation and duration of growth in the presence of CP.
