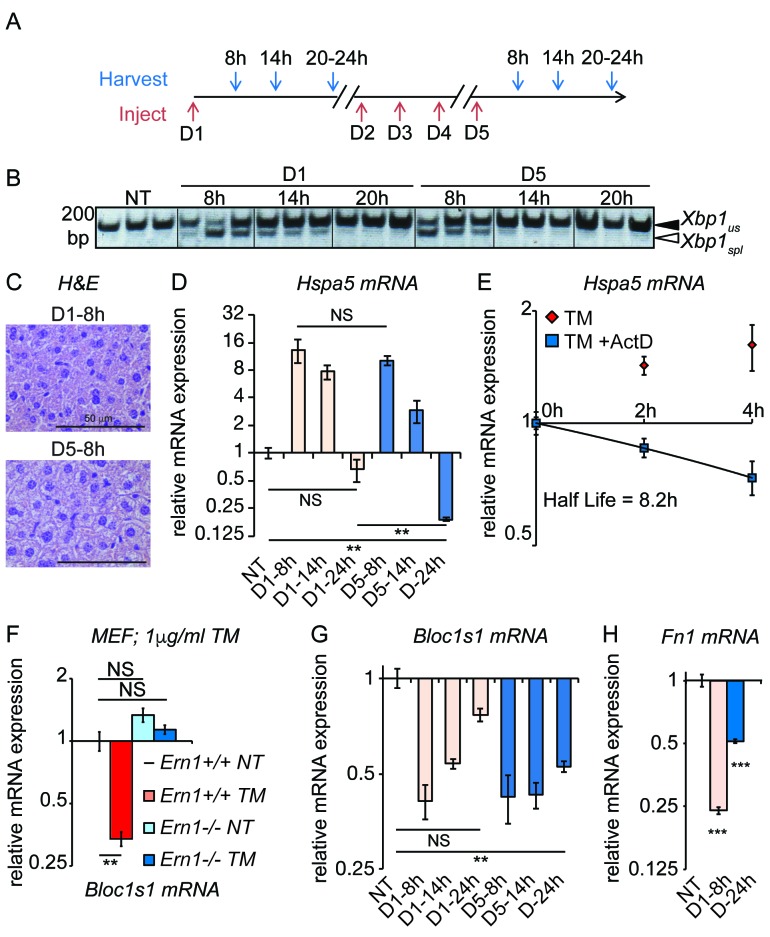
Figure 4. Accelerated degradation diminishes Hspa5 mRNA levels during chronic stress.
(A) Schematic showing treatment protocol; livers were harvested 8, 14, or 20–24 hr after either the first TM injection or the fifth. (B) Conventional RT-PCR was used to distinguished spliced (spl) from unspliced (us) Xbp1 mRNA in samples treated as in (A). Image is inverted black-to-white for greater visual clarity. Each lane represents a separate animal. (C) H and E staining of liver sections harvested at the D1-8h or D5-8h timepoints. (D) Hspa5 mRNA expression was assessed by qRT-PCR from samples treated as in (B). n = 3–4 animals per group (E) Primary hepatocytes were isolated from a wild-type mouse, and treated with TM in the presence or absence of actinomycin D (ActD) to inhibit transcription as described in Materials and methods. Hspa5 half-life was calculated from these data. n = 3 plates/group (F) Wild-type or Ern1-/- (lacking IRE1α) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were treated with TM for 8 hr and expression of the RIDD target Bloc1s1 was determined by qRT-PCR. n = 3 plates/group (G) Animals were treated as in (A) and Bloc1s1 expression was detected by qRT-PCR. (H) Animals were treated for 8 hr or 5d with 0.025 mg/kg TM. Expression of Fn1 was determined by qRT-PCR. n = 4 animals/group.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.20390.009