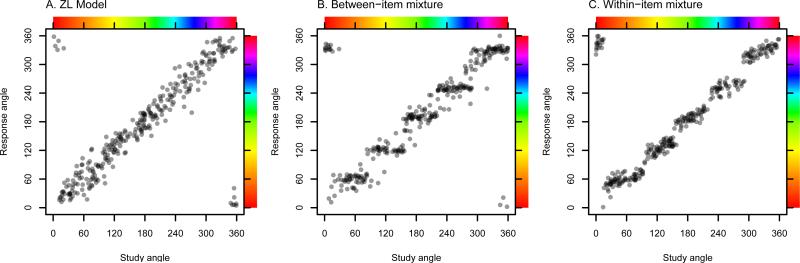
Figure 3.
Data generated from A. the ZL model, B. the between-item variant of our model (the primary model), and C. the within-item variant of our model. No guesses are plotted: Only the memory distributions. For the ZL model, response angles are centered on the studied angle with some error. For the between-item model, responses are either categorical and appear as horizontal steps or continuous and, like the ZL model, are centered around the studied angle. For the within-item model, responses are a mixture of categorical and continuous information, which results in responses that are between the fully categorical flat stair step and the fully continuous line of ideal responding (an intercept of 0 and a slope of 1).