Figure 2.
Rad52 Is Recruited to Sites of DRS
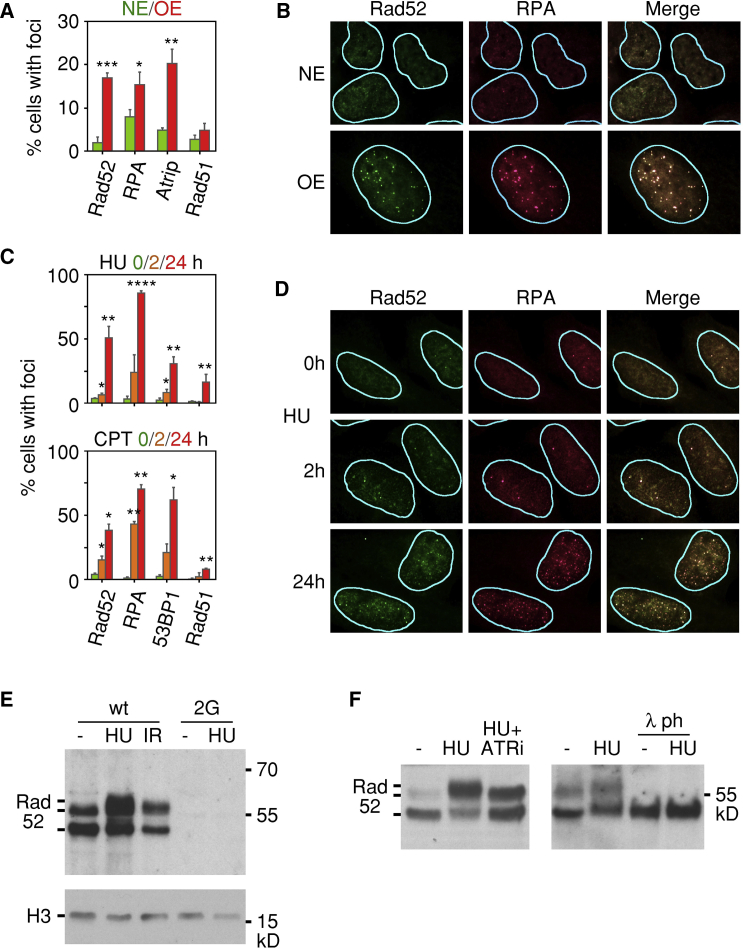
(A) Means and standard deviations of the percentages of cells displaying Rad52, RPA, Atrip, or Rad51 foci in the presence of normal (NE) or high (OE) levels of cyclin E. The results are derived from three independent experiments.
(B) Representative immunofluorescence images showing colocalization of Rad52 and RPA foci in cells overexpressing cyclin E (OE).
(C) Means and standard deviations of the percentages of cells displaying Rad52, RPA, 53BP1, or Rad51 foci following treatment with HU or CPT for 0, 2, or 24 hr. The results are derived from three independent experiments.
(D) Representative immunofluorescence images showing colocalization of Rad52 and RPA foci in cells treated with HU for 24 hr.
(E) Posttranslational modifications of chromatin-bound Rad52 in cells treated with hydroxyurea (HU) for 24 hr or exposed to ionizing radiation (IR). U2OS parental cells (WT) and clone 2G with both alleles of RAD52 inactivated were cultured in the presence of tet to maintain normal levels of cyclin E. The bands corresponding to Rad52 are indicated.
(F) ATR dependence of HU-induced posttranslational modification of chromatin-bound Rad52. U2OS parental cells were cultured in the presence of HU with or without an ATR inhibitor (ATRi) for 24 hr before being harvested. Tet was present in the media to maintain normal levels of cyclin E. Where indicated, the chromatin extracts were treated with lambda phosphatase (λ ph).