Figure 4.
Rad52 Deficiency Restrains Tumor Growth and Prolongs Survival of Mice with APC Mutations
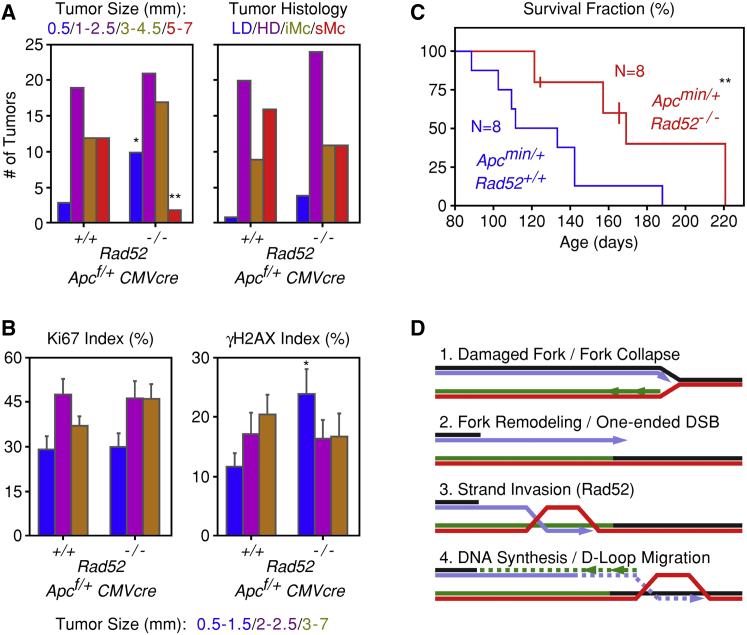
(A) Comparison of tumors present in the intestines of Rad52+/+;Apcf/+;CMVcre (N = 6) and Rad52−/−;Apcf/+;CMVcre (N = 6) mice. Tumors were stratified according to size (in mm) or according to histopathological criteria: LD, low-grade dysplasia; HD, high-grade dysplasia; iMc, intramucosal; and sMc, submucosal.
(B) Proliferation (Ki67) and DNA damage (γH2AX) indices of the tumors present in the intestines of the Rad52+/+;Apcf/+;CMVcre and Rad52−/−;Apcf/+;CMVcre mice. Means and standard deviations of the indices were calculated after stratifying the tumors into three groups according to size.
(C) Survival fractions of Rad52+/+;Apcmin/+ (N = 8) and Rad52−/−;Apcmin/+ (N = 8) mice. Three of the Rad52−/−;Apcmin/+ mice, indicated by vertical lines in the graph, had not died at the time the data were recorded and were considered censored for the statistical analysis.
(D) Proposed model for the role of Rad52 in BIR.