FIGURE 5.
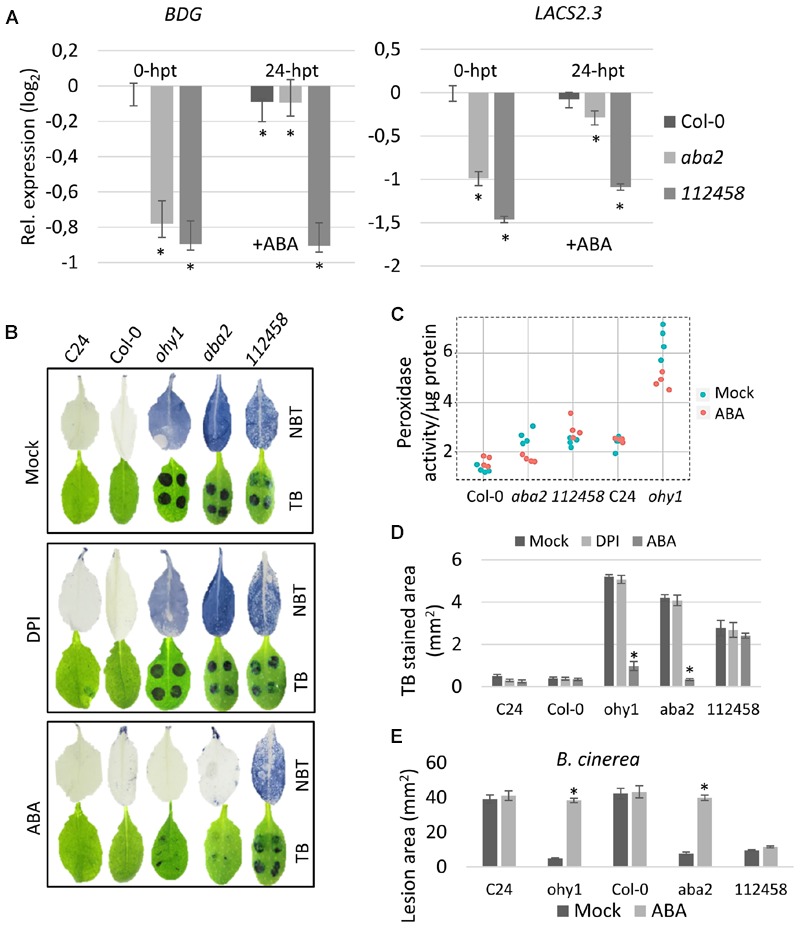
Extensive ROS accumulation and increased peroxidase activity suppress the expression of cutin-biosynthetic genes in ABA mutants. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to analyze the levels of BDG and LACS2.3 transcripts in rosette leaves of 28 day-old aba2 and pyr/pyl 112458 mutants at 24 h after the plants were sprayed with a mock solution or 100 μM ABA. Transcript levels were plotted relative to the expression level in the C24 line at 0-hpt. The EF1α and UBQ10 reference genes were used as internal controls. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates; t-test ∗p < 0.05. (B) Phenotypes of 21-day-old C24, Col-0, ohy1, aba2-1, and pyr/pyl 112458 leaves that were sprayed with 100 μM ABA on developmental days 7 and 14 or with 50 μM DPI on day 20. Superoxide formation was detected using NBT in 21-day-old plants. Cuticle permeability was assessed using TB in 21-day-old plants. (C) The peroxidase activity in ionically bound protein fractions was determined in 28-day-old C24, Col-0, ohy1, aba2-1, and pyr/pyl 112458 plants (n = 4, ±SD). (D) TB-stained areas were quantified in Fiji (n = 4, ±SD, N = 8 in total from two independent experiments). ∗p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (E) C24, Col-0, ohy1, aba2-1, and pyr/pyl 112458 plants were sprayed with a mock solution or 100 μM ABA on developmental days 7 and 14. The plants were subsequently infected with B. cinerea when they were 21 days old. The lesion area was assessed at 3 days post-inoculation (n = 8, ±SD). ∗p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. All experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results.
