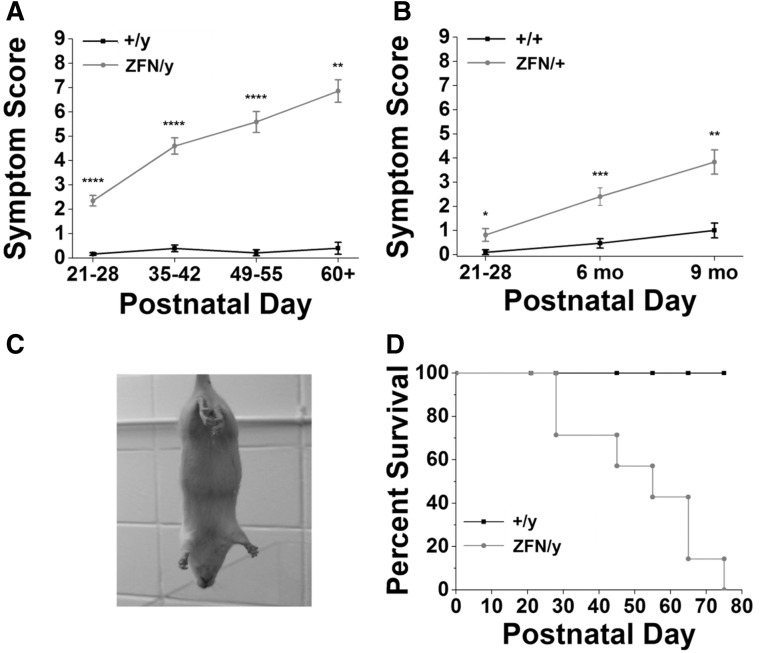
Figure 3.
Mecp2ZFN/y and Mecp2ZFN/+ rats display diminished overall wellness and decreased survival. (A) Mecp2ZFN/y males and (B) Mecp2ZFN/+ females display increased overall symptom scores relative to WTs throughout development (Males: PND 21–28 WT n = 43 Mecp2ZFN/y n = 46; PND 35–42 WT n = 23 Mecp2ZFN/y n = 25; PND 49–55 WT n = 19 Mecp2ZFN/y n = 17; PND 60+ WT n = 5 Mecp2ZFN/y n = 7; Females: PND 21–28 WT n = 10 Mecp2ZFN/+ n = 16; 6 mo WT n = 15 Mecp2ZFN/+ n = 15; 9 mo WT n = 7 Mecp2ZFN/+ n = 12). (C) Representative photograph of hindlimb clasping in an adult Mecp2ZFN/y rat. (D) A Kaplan–Meier survival curve demonstrates that half of Mecp2ZFN/y males have died by PND ∼55 (WT n = 11 Mecp2ZFN/y n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SE, with asterisks representing significant differences (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).