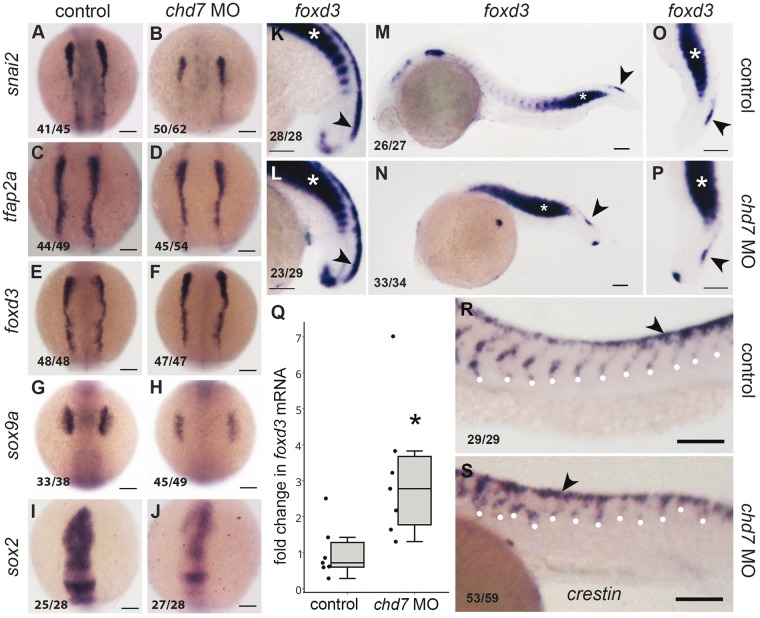
Figure 2.
chd7 knockdown causes differential effects on neural crest markers and impairs neural crest migration. RNA in situ hybridization of neural crest markers at 3 somite (A–J), 18 somite (K–L) and 24hpf (M–P and R–S) stages; control (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O, R) and chd7 morphant (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, P, S) embryos. (A,B) snai2, the earliest marker of neural crest specification was downregulated in chd7 morphant, while early neural crest markers tfap2a (C,D) and foxd3 (E,F) appeared unaffected. (G, H) sox9a was downregulated in the chd7 morphants. (I, J) sox2, a marker of neural tube, was downregulated in the chd7 morphants. Dorsal views, with anterior to the top (A–J). (K,L) At 18hpf, the somitic (white asterisk) and crest expression (black arrowhead) of foxd3, was upregulated in morphants. (M–P) However at 24hpf, foxd3 was predominantly upregulated in somites (white asterisks) while the expression in caudal neural crest was unchanged (black arrowheads) in chd7 morphants. (O,P) magnified views of trunk region of m, n. (Q) Quantitative real time PCR analysis of foxd3 mRNA shows upregulation in 24hpf chd7 morphant embryos (3.13 fold, P < 0.05). (R,S) crestin-marked neural crest cells migrate robustly in controls but are stalled near the dorsal crest in chd7 morphants (white dots mark the point of migration). Lateral views with anterior to the left, dorsal to the top (K–P, R–S). All scale bars are 100µm. The numbers in the bottom left corner indicate the actual number of embryos of the total represented by the image.