Figure 4.
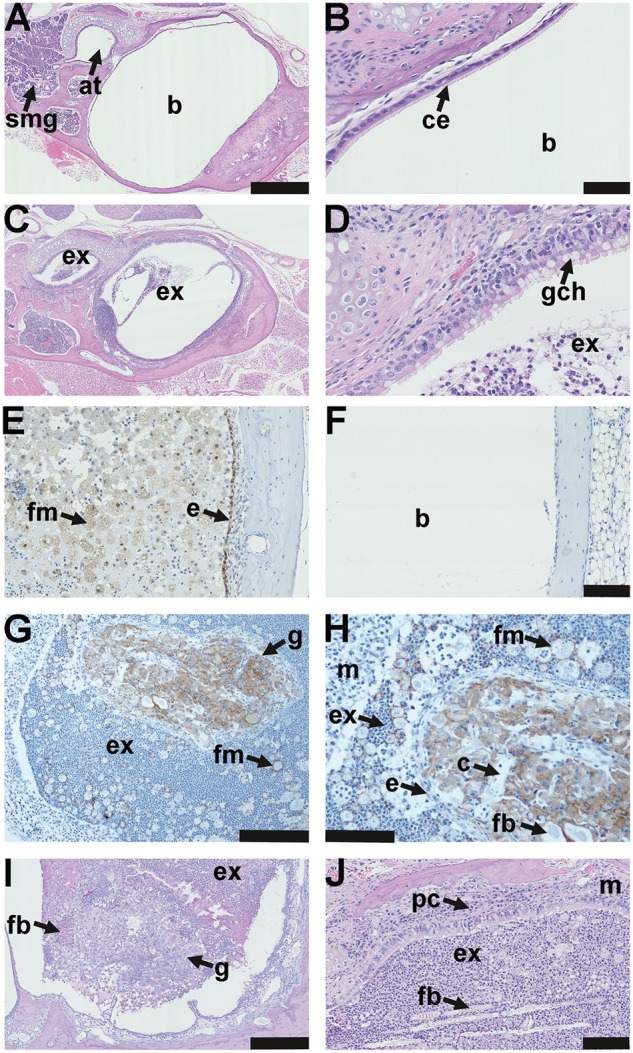
Pathology of the auditory bulla in EDA pathway deleted mice. (A) The healthy air filled bulla (b) and auditory tube (at) in a 37-week-old FVB mouse; note auditory tube submucosal glands (smg). (B) Higher magnification image (A) shows the bulla mucosa in the region adjacent to the auditory tube opening has ciliated epithelium (ce). (C) A 43-week-old EdaTa mouse with otitis media has exudate (ex) in the bulla lumen and auditory tube and (D) epithelium adjacent to the auditory tube opening, has goblet cell hyperplasia (gch). (E, F) In vivo labelling with the hypoxia tracer pimonidazole shows positive staining in epithelium (e) and bulla foamy macrophages (fm) in a representative 16-week-old EdaTa mouse. (F) Hypoxia signals are absent in the healthy air-filled bulla of a representative 8-week-old FVB control mouse. (G, H) The caudal bulla lumen of an 11-week-old EdardlJ/dlJ mouse has an organized vascular granuloma (g) surrounded by exudate (ex) containing neutrophils and foamy macrophages (fm); bulla mucosa (m). (H) Higher magnification of image (G) shows the granuloma has an epithelial margin (e), embedded foreign body (fb) and capillaries (c). Macrophages in the granuloma and foamy macrophages (fm) in bulla exudate stain positively for F4/80. (I) A granuloma located in the caudal bulla of a 14-week-old EdaTa mouse has PAS positive (plant-based) foreign body particle (fb) at the margin. (J) Hair shaft fragments (fb) in the neutrophil rich exudate (ex) of a 43-week-old EdaTa mouse; note plasma cell (pc) infiltration of the thickened bulla mucosa (m). Scale bars: 500 µm (A,C); 50 µm (B,D); 100 µm (E,F,H,J), 200 µm (G) 250 µm (I).
