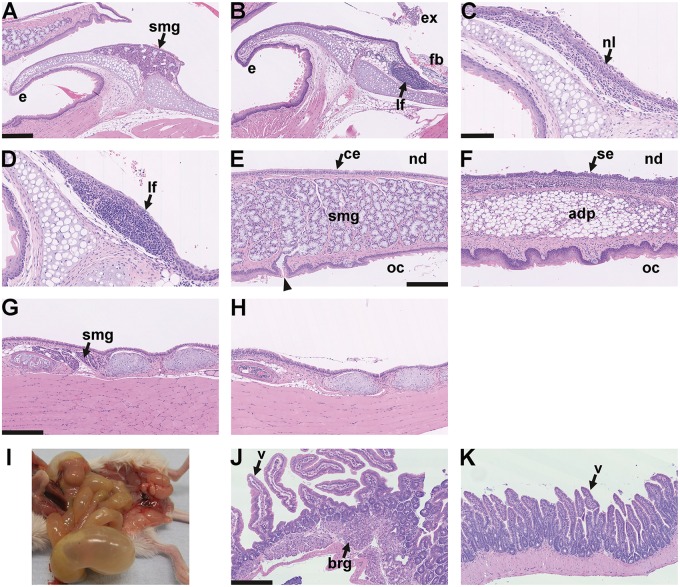
Figure 8.
Larynx histology and aerophagia in EDA pathway deleted mice A–D larynx mid-sagittal plane. (A) The epiglottis (e) of a 24-week-old FVB mouse has submucosal glands (smg) but these are absent in EdardlJ/dlJ and EdaTa mice. (B) The epiglottis of 14-week-old EdardlJ/dlJ mouse lacks glands and has a submucosal lymphoid follicle (lf). There is exudate (ex) and foreign body (fb) in the proximal trachea. (C,D) Two 25-week-old mice EdaTa mice. (C) One EdaTa mouse has neutrophil (nl) infiltration of the epiglottis epithelium. (D) a higher magnification image of a submucosal lymphoid follicle (lf) in a second EdaTa mouse. (E,F) Soft palate mid-sagittal plane. (E) The soft palate of a 24-week-old FVB mouse has submucosal gland comprising mucous cells (smg) that empty via ducts (arrow head) into the oral cavity (oc); nasopharynx (nd) is lined by ciliated epithelium (ce). (F) The soft palate of a 14-week-old EdardlJ/dlJ mouse lacks submucosal glands and this region is occupied by adipose tissue (adp); the nasopharynx is lined by squamous epithelium (se). (G,H) Trachea mid-sagittal plane. (G) The proximal trachea of a 14-week-old EdardlJ/+ mouse has submucosal glands (smg); (H) these glands are absent in a 25-week-old EdaTa mouse. (I) Post mortem appearance of an 18-week-old EdaTa mouse with aerophagia that has an air filled stomach, small intestines and caecum. (J,K) small intestine. (J) Duodenum of this EdaTa mouse has a normal submucosal Brunner’s gland (brg) and villi (v); (K) the jejunum has an empty lumen. Scale bars: 250 µm (A,B,E–H,J,K); 100 µm (C,D).