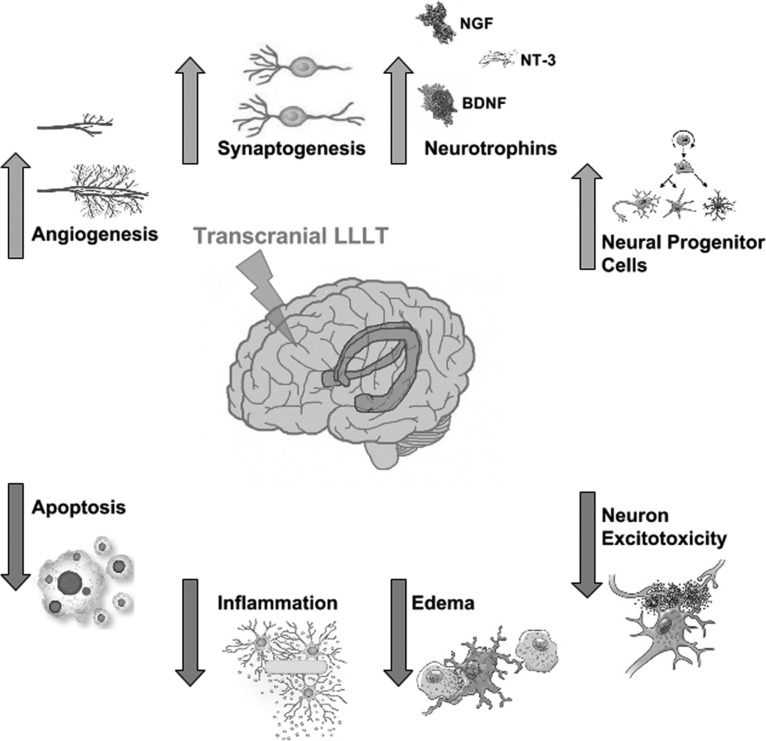
FIG. 1.
Molecular mechanisms of transcranial LLLT. Light passes through the scalp and skull, where it is then absorbed by cytochrome c oxidase in the mitochondrial respiratory chain of the cortical neurons in the brain. Cell signaling and messenger molecules are upregulated as a result of stimulated mitochondrial activity, including ROS, NO, and ATP. These signaling molecules activate transcription factors, including NF-κB and AP-1, which enter the nucleus and cause transcription of a range of new gene products. AP-1, activator protein 1; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; LLLT, low-level laser therapy; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NGF, nerve growth factor; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species.