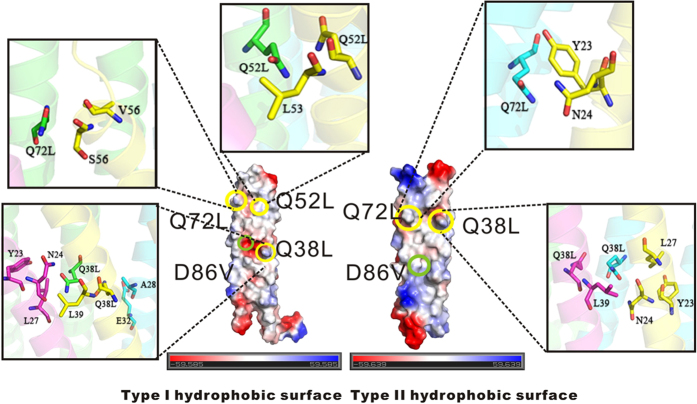
Figure 4. Specific Point mutations on PhaPAh.
Residues of PhaPAh were chosen for mutagenesis based on the presence of hydrophilic amino acids within a predominantly hydrophobic surface. Mutants Q38L, Q52L, Q72L and D86V were designed to investigate the variation of surfactant properties. In chain A, which has a type I hydrophobic surface, the mutant Q38L can form hydrophobic interactions with Y23, N24 and L27 from chain C, mutant Q38L and the wild-type residue L39 from chain D, as well as A28 and E32 from chain B. Mutant Q52L can form hydrophobic interactions with mutant Q52L and the wild-type residue L53 from chain D. The mutant Q72L can form hydrophobic interactions with residues V56 and S57 from chain D. Chain D also has a type I surface. While the mutant Q38L in chain B forms hydrophobic interactions with Y23, N24 and L27 from chain D and mutants Q38L and L39 from chain C, the mutant Q72L in chain B forms hydrophobic interactions with residues Y23 and N24 from chain D. The chains B and C both have a type II surface.