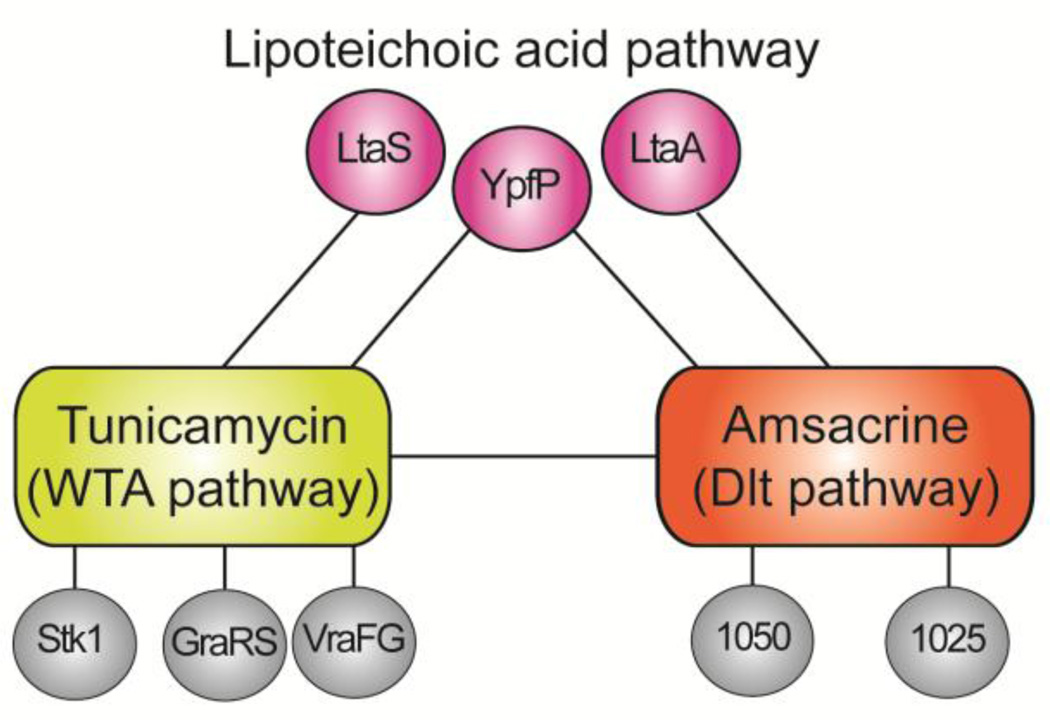
Figure 3.
Schematic showing selected synthetic lethal interactions between three cell envelope pathways in Staphylococcus aureus. Synthetic lethal interactions were identified by probing a high density transposon mutant library with tunicamycin, which inhibits TarO and prevents WTA synthesis, and amsacrine, which inhibits DltB and prevents D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acids. Inhibiting D-alanylation is lethal to mutants that make abnormal LTA due to deletion of ypfP or ltaA, but not to mutants that make no LTA (ΔltaS strains). Information on synthetic lethal interactions between the Dlt pathway and other pathways enabled design of a strain panel diagnostic for Dlt pathway inhibitors (see Figure 4).