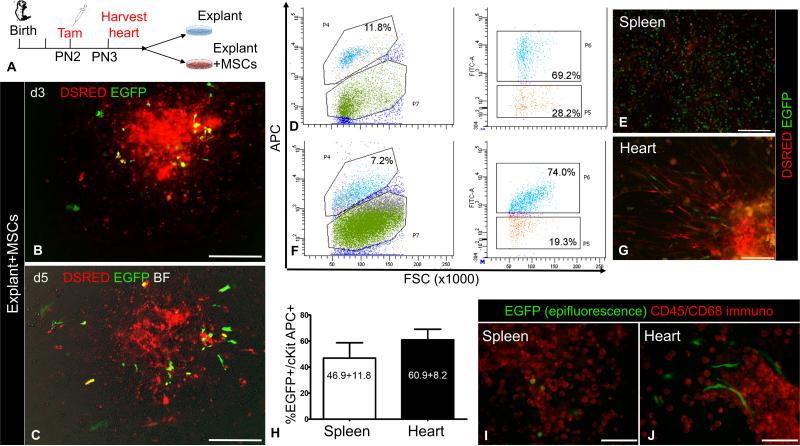
Figure 2. MSCs stimulate outgrowth of CSCs from cardiac explants.
A, Schematic of the ex-vivo lineage-tracing experiments to assess the effect of MSCs on cKit+ cardiac cells. B-C, Ex-vivo culture of a cKitCreERT2/+;IRG myocardial explant on days (d)3 (B) and d5 (C), after co-culture with MSCs.. D, Representative flow cytometric analysis of EGFP and cKit-APC co-localization in the spleen. E, Live epifluorescence imaging of EGFP and DSRED in spleen cells of panel A, prior to FACS analysis. F, Representative flow cytometric analysis of EGFP and cKit-APC co-localization in the heart. G, Live epifluorescence imaging of EGFP and DSRED in heart cells of panel C, prior to FACS analysis. H, summary of Cre-mediated recombination efficiency in cKit+ cardiac and spleen cells (n=3 per group). I, Immunostaining of neonatal spleen explant-derived cells with a cyanine-5 CD45/CD68 antibody cocktail (pseudocolored red). All spleen EGFP+ cells have a blast-like morphology and exhibit strong CD45/CD68 immunoreactivity. J, Immunostaining of neonatal cardiac explant-derived cells from the same mouse, with a cyanine-5 CD45/CD68 antibody cocktail. All cardiac EGFP+ cells have a spindle cell-like morphology and are negative for CD45/CD68. Scale bars, 200μm.