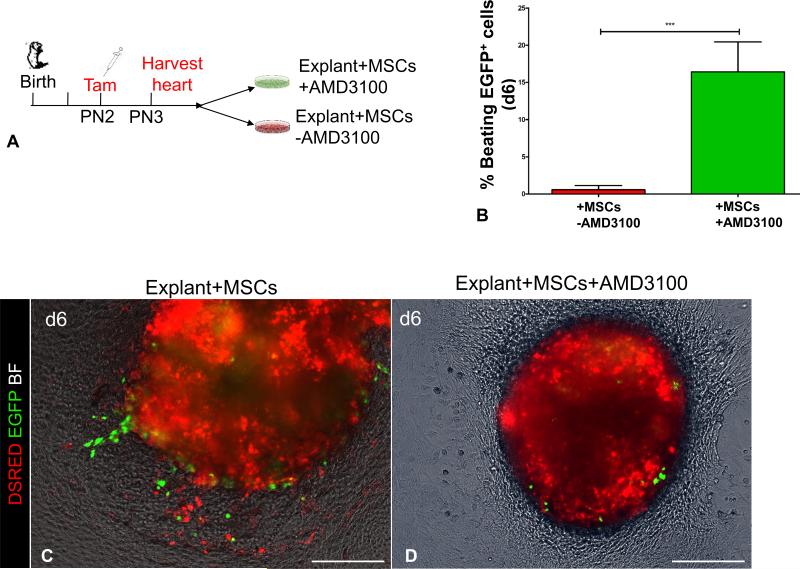
Figure 5. AMD3100 disables chemotactic responsiveness of CSCs to MSCs and promotes cardiac differentiation.
A, Schematic of the ex-vivo genetic fate-mapping strategy to assess the role of SDF1/CXCR4 signaling pathway in MSCs-CSCs interactions. cKitCreERT2/+;IRG neonates (n=2 neonates; 3 myocardial explants/neonate/time point) were pulsed with tamoxifen at PN2; on PN3 heart tissue was explanted and cultured ex-vivo on MSCs-coated vessels in the presence or absence of AMD3100. The migratory activity of CSCs was assessed as the outgrowth of EGFP+ myocardial cells from within the explanted tissue into the coated surface of the culture vessel. B, Inhibition of the chemotactic responsiveness to MSCs by AMD3100, dramatically enhances differentiation of EGFP+ cells into spontaneously beating derivatives.. C, A myocardial explant cultured on MSCs feeders for five 6 days. D, Supplementing the growth medium with AMD3100 inhibits migration of EGFP+ cells. AMD, AMD3100. Data are presented as mean±SEM. ***p≤0.0001. Scale bars, 150μm.