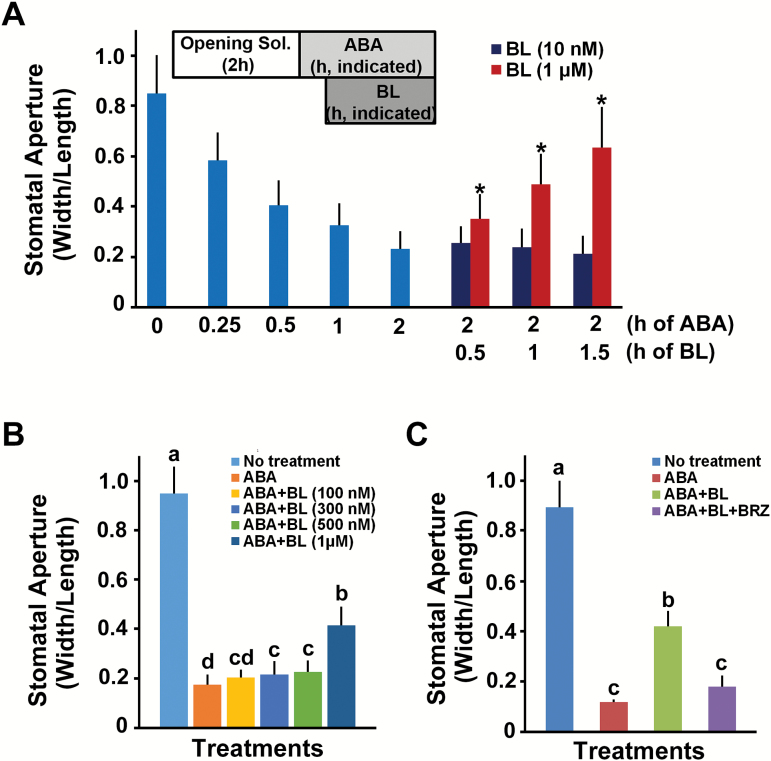
Fig. 3.
High concentrations of BL inhibited the ABA-induced stomatal closure. (A) ABA-induced stomatal closure was measured with or without BL treatment for indicated times. Low (10 nM) or high (1 μM) concentrations of BL were added to the ABA-containing solution for the indicated times. Experiments were independently repeated three times (n=50 each time). Error bars indicate standard errors (*P<0.0001, compared with the corresponding samples treated with ABA only). (B) Effects of BL concentrations on the inhibition of ABA-induced stomatal closure. Different concentrations of BL were added to the ABA-containing solution for 1.5 h. Experiments were independently repeated twice (n=30 each time). (C) Effect of BRZ on BL inhibition of ABA-induced stomatal closure. BRZ (1 μM) was applied 30 min after BL (1 μM) to the ABA-containing solution. Experiments were independently repeated twice (n=30 each time). In all experiments, 1 μM ABA was used. Error bars indicate standard errors. In (B) and (C), values labeled with different letters are statistically different analysed by one-way ANOVA (P<0.05). (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)