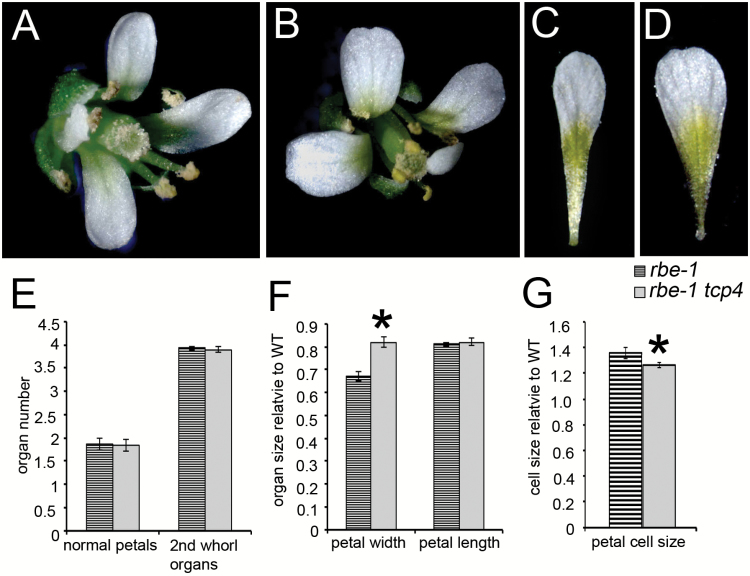
Fig. 3.
tcp4 partially rescues the petal phenotypes of rbe-1. (A) a rbe-1 flower, (B) a rbe-1 tcp4 flower, (C) a rbe-1 petal, (D) a rbe-1 tcp4 petal. (E) Numbers of normal petals and second whorl organs in flowers 5–20 for rbe-1 and rbe-1 tcp4 (n=30; mean±SEM). (F) Measurements of petal width and length in flowers 5–20 for rbe-1 and rbe-1 tcp4. Petal sizes were normalized to the values of the L er control (n=20; mean±SEM). Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the single and double mutants (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA with Tukey test). See Supplementary Table S2 for the details of statistical analyses. (G) Measurements of petal cell size of rbe-1 and rbe-1tcp4. Cell size was normalized to the wild type value (n=10; mean±SEM). Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the single and double mutants (P < 0.05, Student t test).
(This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)