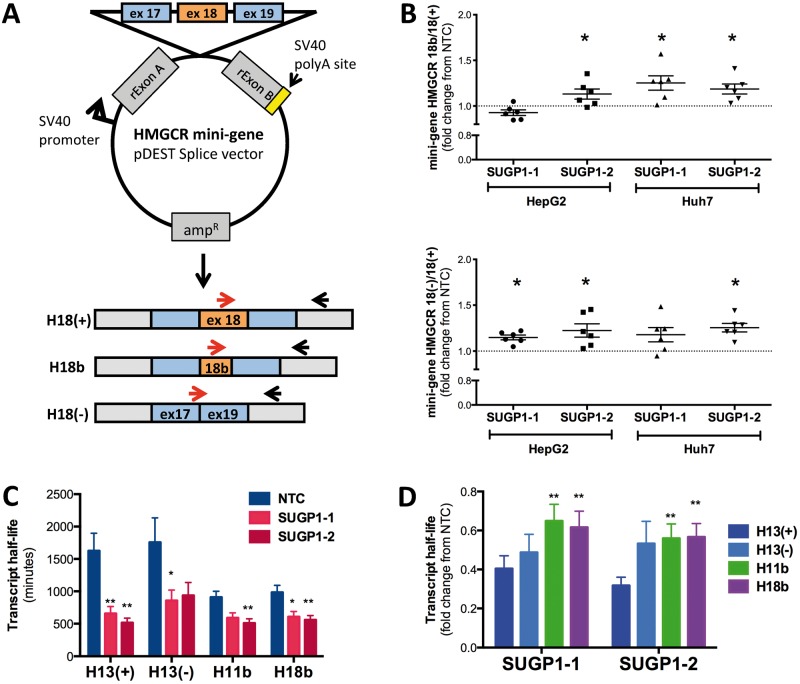
Figure 4.
SUGP1 knockdown modulates HMGCR alternative splicing and transcript half-life. (A) Diagram of the mini-gene construct and quantitative PCR (qPCR) primers used to directly test SUGP1 effects on HMGCR exon 18 alternative splicing. Red arrows indicate different forward primers within the cDNA sequence used to assay for alternative splice variants. (B) Mini-gene-derived HMGCR transcript ratios show an increase in alternative splice variants upon SUGP1 knockdown. HepG2 and Huh7 cells were first transfected with SUGP1-1, SUGP1-3 or NTC siRNAs. After 24 hours, cells were transfected with the HMGCR exon 18 containing mini-gene construct and incubated for an additional 24 hours. Mini-gene-derived HMGCR transcripts were quantified by qPCR (n = 6 per condition). (C) SUGP1 knockdown decreases transcript half-life. HepG2 cells were transfected with SUGP1 or NTC siRNAs, and actinomycin D was added after 48 hours to halt cellular transcription. HMGCR transcript levels were quantified over 24 hours, and half-life calculated as previously described. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (D) Relative changes in HMGCR transcript half-life in cells transfected with one of the two SUGP1 siRNAs compared to NTC. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 indicate effects of SUGP1 knockdown decrease HMGCR11b and HMGCR18b transcript half-life compared to HMGCR13(+). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.