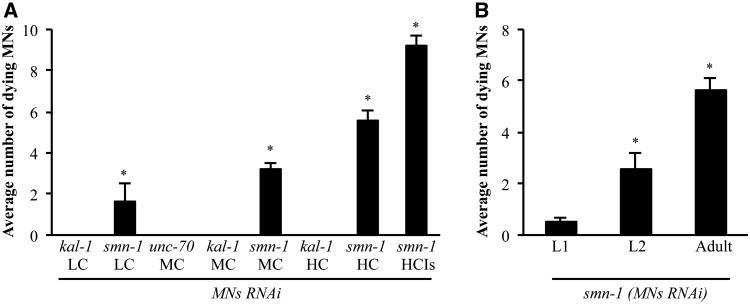
Figure 4.
Quantification and temporal characterization of motor neuron death induced by smn-1(MNs RNAi). (A) Accumulation of fluorescence in D-type motor neurons in the ventral cord of smn-1(MNs RNAi) animals is dependent on the transgene dose. Number of motor neurons accumulating fluorescence in transgenic animals. Bars represent the average number of fluorescence accumulating neurons per animal and for each transgenic strain the results shown are the mean of those obtained from animals of at least two independent line ± S.E.M.; >280 animals were observed for kal-1(MNs RNAi LC), >500 animals were observed for smn-1(MNs RNAi LC), 100 animals were observed for each transgenic strain at MC, >150 animals were observed for each transgenic strain at HC, and 100 animals were observed for the smn-1(MNs RNAi) integrated line (HCIs). * indicates significantly different from unc-70(MNs RNAi) and kal-1(MNs RNAi) (P < 0.001, non-parametric Mann–Whitney test). (B) The number of motor neurons accumulating fluorescence increases with ageing. Bars represent the average number of fluorescence-accumulating neurons per animal. L1 is the first larval stage after hatch. L2 is the subsequent larval stage. >20 animals were observed at the L1 stage, 50 animals were observed at the L2 stage, and 130 animals were observed at the adult stage. * indicates significantly different from previous larval stage (P < 0.001, non-parametric Mann–-Whitney test). Transgenic strains were obtained using an HC of interfering construct.