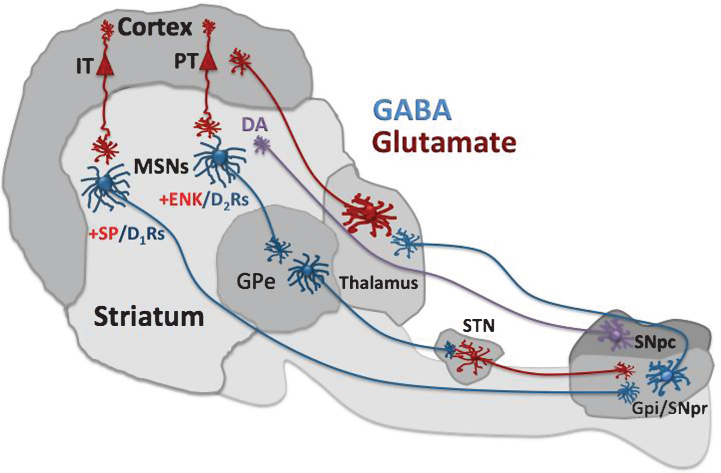
Fig.1.
Schematic illustration of basal ganglia circuitry. Striatal medium spiny neurons (MSNs) receive excitatory corticostriatal input from IT and PT pyramidal neurons in cerebral cortex. Intra-telencephalic (IT) neurons preferentially activate substance P/D1 receptor (SP/D1R) MSNs that project to the internal globus pallidus and sustantia nigra pars reticulata (GPi/SNpr) forming the direct pathway. Pyramidal tract (PT) neurons activate enkephalin/D2 receptor (ENK/D2R) MSNs that form the indirect pathway and send projections to the external globus pallidus (GPe). GPe neurons in turn send axons to the subthalamic nucleus (STN), which projects to GPi/SNpr. GPi/SNpr is the basal ganglia output system that integrates direct and indirect pathway information and sends it back to cortex via thalamus.