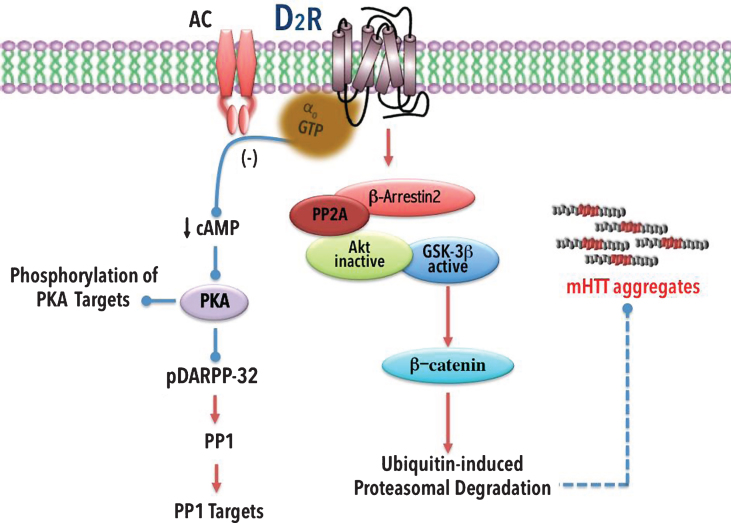
Fig.4.
Alteration of the D2 receptor signaling pathway in HD. D2 receptor activation decreases cAMP signaling. D2 receptors can also activate β-arrestin2, which recruits phosphatase-2A (PP2A). PP2A in turn interacts with thymoma viral protoncogen (Akt). The PP2A-Akt complex promotes activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 β (GSK-3β), which induces phosphorylation of β-catenin, a protein involved in the activation of the ubiquitin-induced proteasomal degradation system [209, 210]. Because GSK-3β expression is decreased in HD [90, 207] the decrease in phosphorylated β-catenin causes cellular toxicity [211]. Decreased activation of D2 receptors may be involved in the reduced degradation of mHTT. Stimulatory effects are indicated with arrows; inhibitory effects with a line ending in a circle. Broken lines indicate possible mechanism of action.