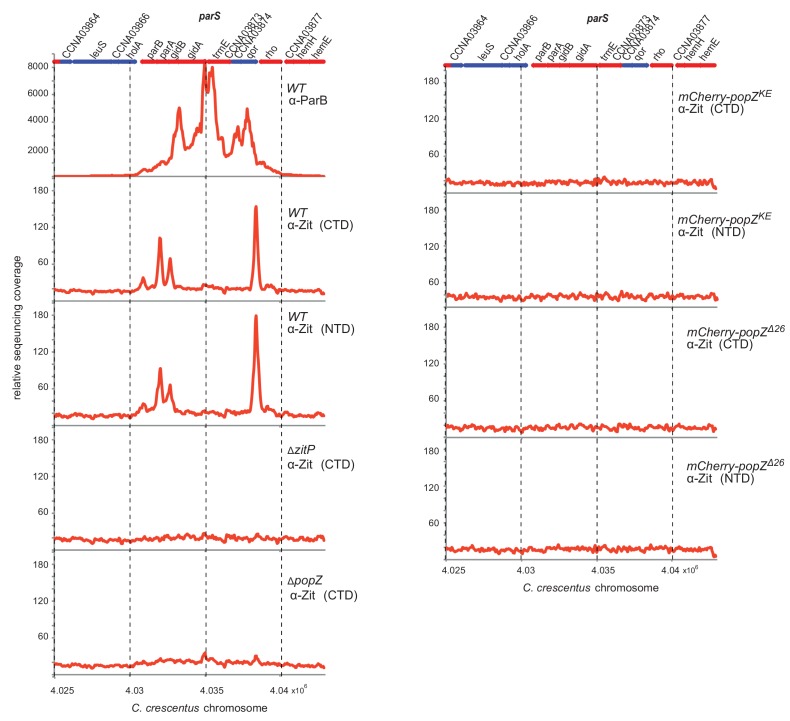
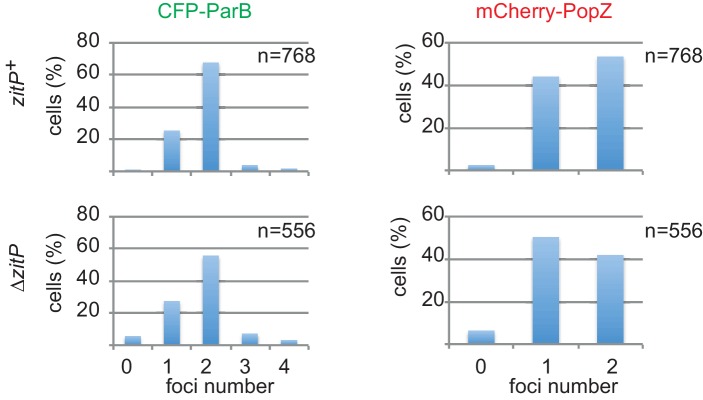
Figure 4. The ZitP•PopZ complex controls the C.
crescentus cell division cycle. (A) Overlays of mCherry-fluorescence and phase contrast images of WT (upper panels) or ΔzitP (bottom) C. crescentus expressing the mCherry-PopZKE variant that no longer interacts with ParB. mCherry-PopZKE is expressed from the native locus (mCherry-popZKE) in lieu of untagged PopZ. Below the micrographs are quantifications of cells with and without bipolar or monopolar fluorescent foci of mCherry-PopZKE. (B) Efficiency of plating (EOP) assays of C. crescentus strains expressing WT mCherry-PopZ (mCherry-popZ) or variants that no longer interact with ParB (mCherry-popZKE), with ParA (mCherry-popZSP) or both (mCherry-popZKEP and mCherry-popZΔ26) in WT or ΔzitP cells. Serial ten-fold dilutions were plated on PYE agar containing spectinomycin. (C) Growth measurements of various strains monitored by optical density at 660 nm (OD660) in PYE. (D) Overlays of CFP- and mCherry-fluorescence with phase contrast images from C. crescentus popZ::mCherry-popZ parB::CFP-parB cells harbouring an empty plasmid (pMT464, left panel) or the pPxyl-ZitP1-133(WT) derivative followed by time-lapse analysis with images acquired every 40 min. (E) Overlays of mCherry-fluorescence with phase contrast images from C. crescentus popZ::mCherry-popZ parB::CFP-parB cells harbouring an empty plasmid (pMT464, left panel) or derivatives: pPxyl-ZitP1-133(WT) (second panel), pPxyl-ZitP1-133(CS) (third panel), pPxyl-ZitP1-133(W35I) (fourth panel) and pPxyl-ZitP1-133(R24A/R27A) (right panel). Overexpression of ZitP1-133 variants was induced with xylose 0.3% for 6 hr prior to imaging. (F) Overlays of mCherry-fluorescence with phase contrast images from C. crescentus popZ::mCherry-popZ parB::CFP-parB cells harbouring a Pxyl-ZitP1-133(MalF-TM), Pxyl-ZitP1-133(WT) or a Pxyl-ZitP1-90 overexpression plasmid. Overexpression was induced by growth in 0.3% xylose for 6 hr prior to imaging. (G) Overlays of mCherry-fluorescence with phase contrast images from C. crescentus popZ::mCherry-popZKEP parB::CFP-parB cells harbouring a Pxyl-ZitP1-133(WT) or a Pxyl-ZitP1-133(W35I) overexpression plasmid. Overexpression was induced by growth in 0.3% xylose for 6 hr prior to imaging.