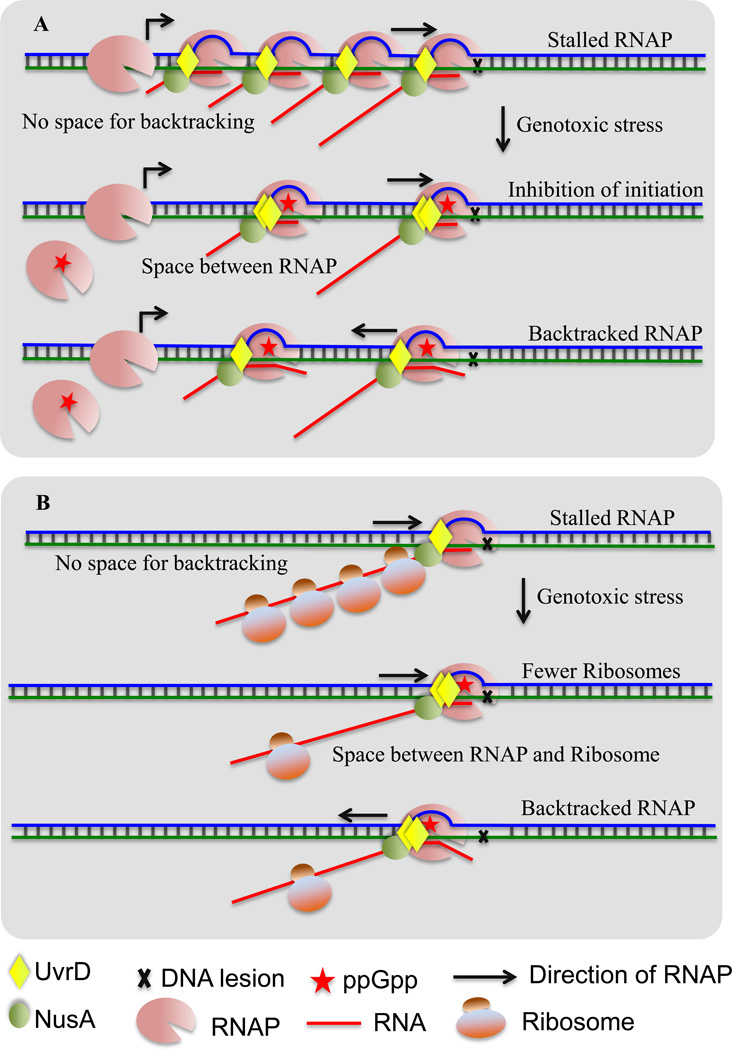
Figure 2. Possible indirect activities of ppGpp that promote backtracking.
(A) ppGpp may facilitate TCR at ribosomal operons during genotoxic stress by partially suppressing initiation at their promoters. Top: When RNAP encounters a lesion in the highly transcribed rRNA genes it cannot backtrack due to tightly packed arrays of RNAP molecules. Such arrays would also be resistant to Mfd- and Rho-dependent termination. Middle: Transient accumulation of ppGpp during genotoxic stress may partially inhibit initiation at rrn operons thereby reducing the number of elongating RNAPs. This should increase the space between adjacent RNAPs and create room for backtracking. Bottom: RNAP can now backtrack at the site of damage to enable TCR.
(B) ppGpp can promote TCR by controlling the number of ribosomes during genotoxic stress. Top: Ribosomes act as anti-backtracking factors [44]. Middle: ppGpp can diminish the number of ribosomes, thereby increasing the probability of uncoupling transcription from translation. Bottom: Fewer ribosomes increase the probability of backtracking.