Table 1. Sperm DNA fragmentation (SDF) testing methods.
| Test | Principle | Advantage | Disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
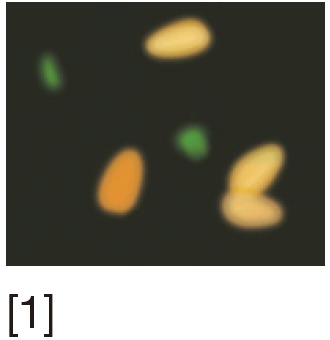 |
AO test | Metachromatic shift in fluorescence of AO when bound to single strand (ss)DNA. Uses fluorescent microscopy | Rapid, simple and inexpensive | Inter-laboratory variations and lack of reproducibility |
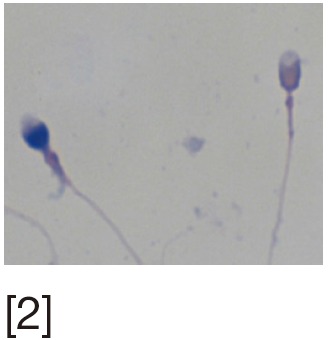 |
AB staining | Increased affinity of AB dye to loose chromatin of sperm nucleus. Uses optical microscopy | Rapid, simple and inexpensive | Inter-laboratory variations and lack of reproducibility |
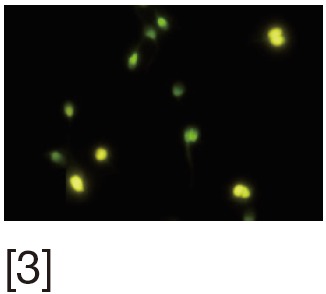 |
CMA3 staining | CMA3 competitively binds to DNA indirectly visualizing protamine deficient DNA. Uses fluorescent microscopy | Yields reliable results as it is strongly correlated with other assays | Inter-observer variability |
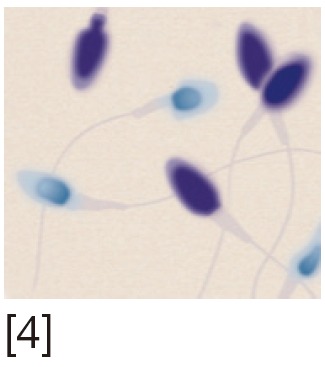 |
TB staining | Increased affinity of TB to sperm DNA phosphate residues. Uses optical microscopy | Rapid, simple and inexpensive | Inter-observer variability |
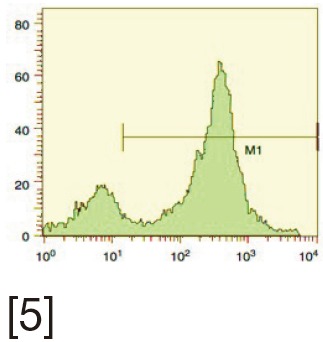 |
TUNEL | Quantifies the enzymatic incorporation of dUTP into DNA breaks. Can be done using both optical microscopy and fluorescent microscopy. Uses optical microscopy, fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry | Sensitive, reliable with minimal inter-observer variability. Can be performed on few sperm | Requires standardization between laboratories |
 |
SCSA | Measures the susceptibility of sperm DNA to denaturation. The cytometric version of AO test. Uses flow cytometry | Reliable estimate of the percentage of DNA-damaged sperm | Requires the presence of expensive instrumentation (flow cytometer) and highly skilled technicians |
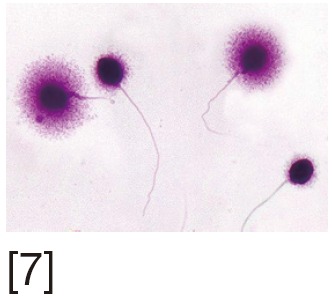 |
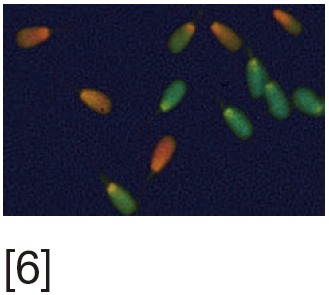
SCD or Halo test | Assess dispersion of DNA fragments after denaturation. Uses optical or fluorescent microscopy | Simple test | Inter-observer variability |
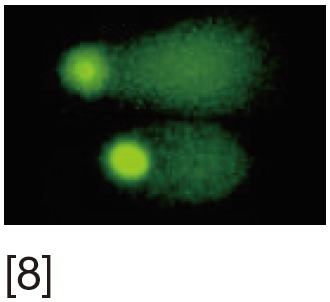 |
SCGE or comet assay | Electrophoretic assessment of DNA fragments of lysed DNA. Uses fluorescent microscopy | Can be done in very low sperm count. It is sensitive and reproducible | Requires an experienced observer. Inter-observer variability |
[1] Acridine orange (AO) stains normal DNA fluoresces green; whereas denatured DNA fluoresces orange-red. [2] Aniline blue (AB) staining showing sperm with fragmented DNA and normal sperm. [3] Chromomycin A3 (CMA3) staining: protamine deficient spermatozoa appear bright yellow; spermatozoa with normal protamine appear yellowish green. [4] Toulidine blue (TB) staining: normal sperm appear light blue and sperm with DNA fragmentation appear violet. [5] Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay fluorescent activated cell sorting histogram showing percentage of SDF. [6] Sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA): flow cytometric version of AO staining. [7] Sperm chromatin dispersion (SCD) test: spermatozoa with different patterns of DNA dispersion; large-sized halo; medium-sized halo [2]; very small- sized halo. [8] Comet images showing various levels of DNA damage.
