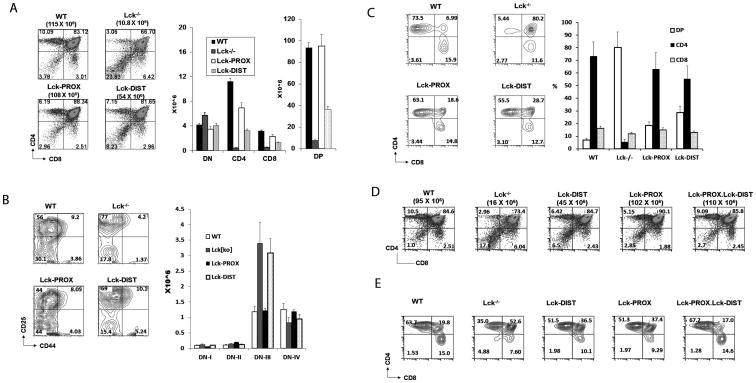
Figure 3.
Effect of lck promoter deletion on thymocytes development. A) Thymocytes from WT, lck-/-, Lck-PROX and Lck-DIST mice were stained with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8, and assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms represent mean +/- SE number of thymocytes of each thymic subpopulation. Statistical analysis is presented in Supporting Figure 1. B) Thymocytes from WT, lck-/-, Lck-PROX and Lck-DIST mice were stained with anti-CD25 and anti-CD44, gated to exclude cells expressing CD4, CD8, NK1.1, Mac-1, Gr1, CD3, or B220, and assessed by flow cytometry. Histograms represent number of thymocytes of each thymic subpopulation. Statistical analysis is presented in Supporting Figure 1. C) Thymocytes from WT, lck-/-, Lck-PROX and Lck-DIST mice were gated on TCR(H57)hi cells and analyzed for CD4 and CD8 expression to identify CD4, CD8, and DP cells (Gating strategy presented in Supporting Fig. 6). Histograms represent number of thymocytes of each thymic subpopulation as mean +/- SE from 3 independent experiments, in each of which single age-matched mice of each genotype were tested. D) Thymocytes from WT, lck-/-, Lck-PROX, Lck-DIST, and double transgenic Lck-PROX.Lck-DIST mice were stained with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8, and assessed by flow cytometry. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments, in each of which single age-matched mice were tested. Statistical analysis is presented in Supporting Figure 3. E) Thymocytes from WT, lck-/-, Lck-PROX, Lck-DIST, and double transgenic Lck-PROX.Lck-DIST mice were gated on TCR(H57)hi cells and analyzed for CD4 and CD8. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments, in each of which single age-matched mice were tested.