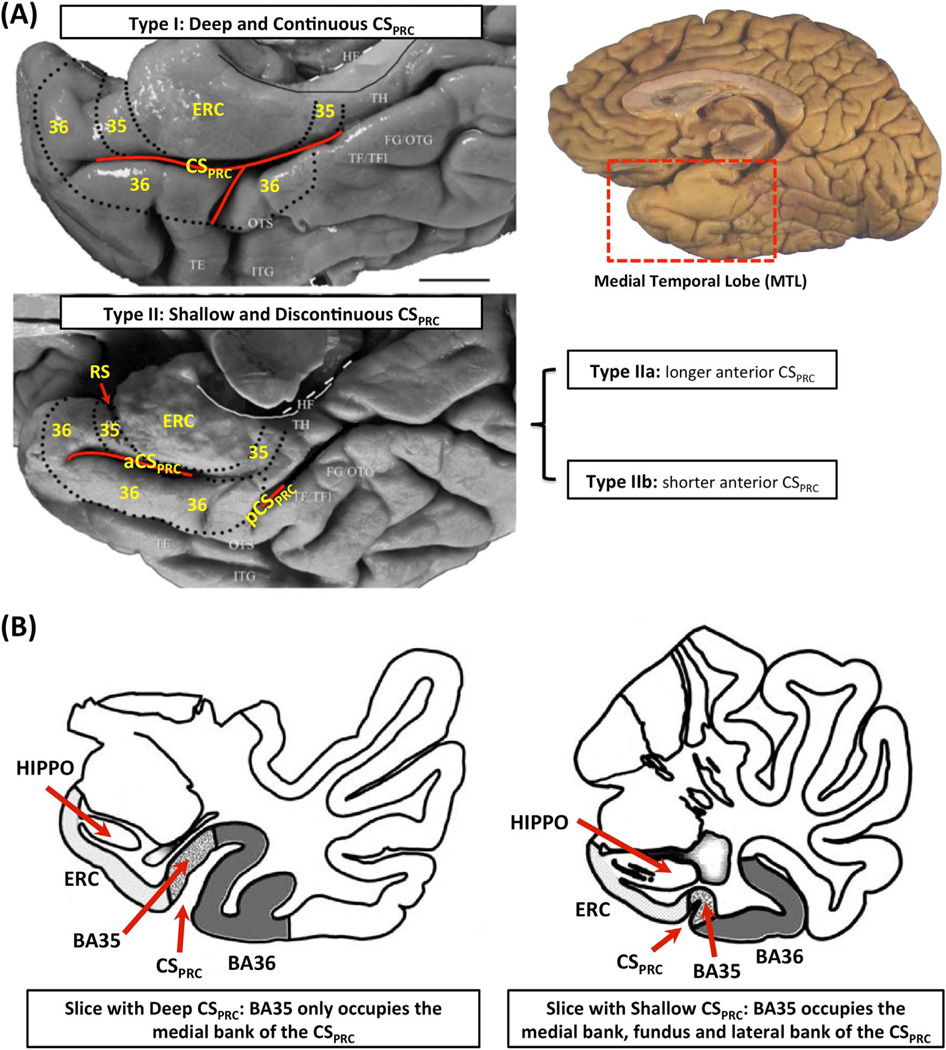
Fig. 1.
(A) Three anatomical variants of the PRC defined by the folding and branching patterns of the collateral sulcus. (B) Two examples in Ding and Van Hoesen (2010) showing that the borders and extent of BA35 and BA36 depend on the depth of CSPRC. Figure adapted from Ding and Van Hoesen (2010). Abbreviations: ERC=entorhinal cortex; 35, 36=Brodmann areas 35 and 36; BA35, BA36=Brodmann areas 35 and 36; PRC=perirhinal cortex; CS=collateral sulcus; CSPRC=the portion of CS adjacent to PRC; aCSPRC/pCSPRC=anterior/posterior CSPRC; HF=hippocampal fissure; RS=rhinal sulcus; FG=fusiform gyrus; HIPPO=Hippocampus; OTG=occipito-temporal gyrus; OTS=occipito-temporal sulcus; ITG=inferior temporal gyrus; TE, TH, TF=temporal areas TE, TH, TF defined in (Von Economo, 1929); TFl=lateral subdivisions of area TF.