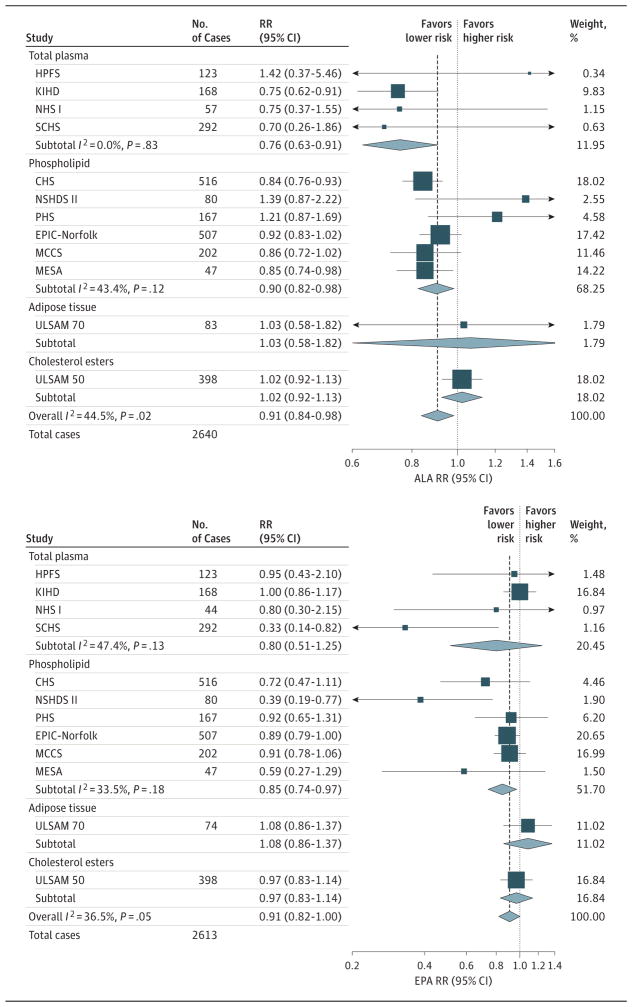
Figure 1.
Relative Risk (RR) of Fatal Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) per 1-SD Increase in the Biomarkers α-Linolenic Acid (ALA; 18:3ω-3) and Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA; 20:5ω-3)
Estimates were pooled using random effects meta-analysis. See eFigure 1 in the Supplement for results using inverse-variance weights. CHS indicates Cardiovascular Health Study20; EPIC-Norfolk, European Prospective Investigation of Cancer (Norfolk)21; HPFS, Health Professionals Follow-up Study23; KIHD, Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study25; MCCS, Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study26; MESA, Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis27; NHS, Nurses’ Health Study30; NSHDS, Northern Sweden Health and Disease Study28,29; PHS, Physician’s Health Study31; SCHS, Singapore Chinese Health Study33; and ULSAM, Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men.35