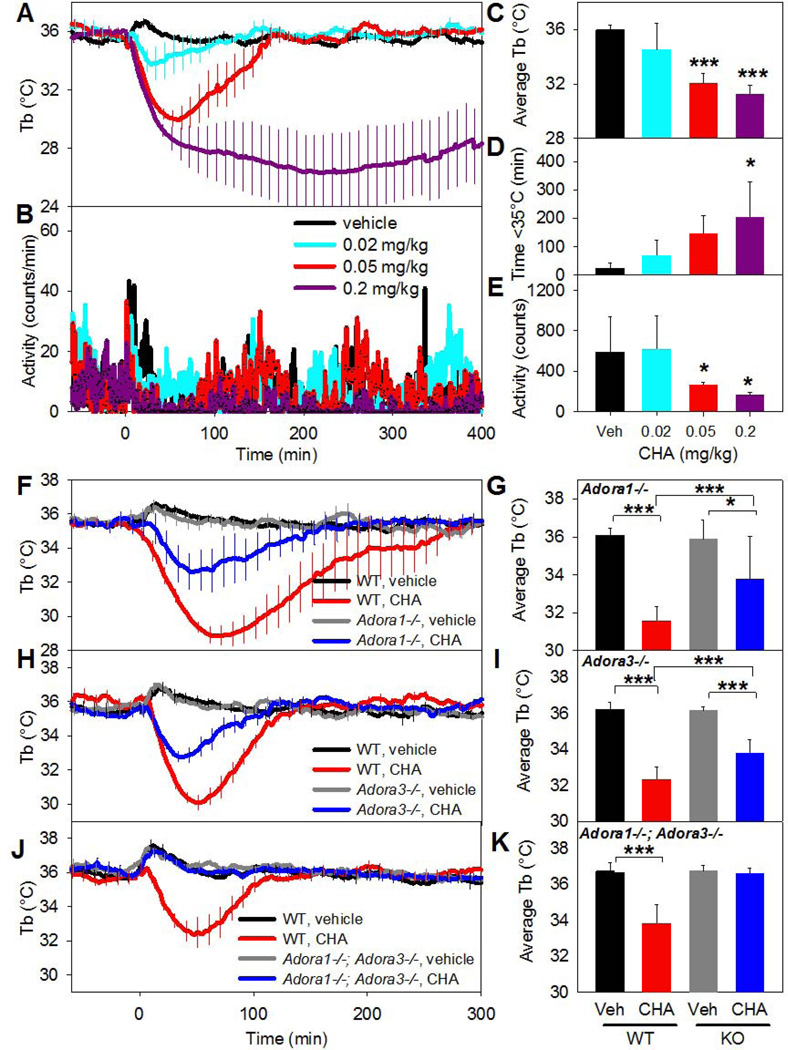
Fig. 1. Systemic CHA causes hypothermia and decreased physical activity through both A1AR and A3AR.
(A, B) Tb and physical activity response to the indicated CHA doses injected i.p. into C57BL/6J mice. (C–E) Effect of CHA on average Tb (0–60 min), duration of hypothermia, and physical activity (10–60 min). Data are mean ± SEM, n=5/group; every tenth SEM is shown in A and SEMs were omitted in B for visual clarity. (F,G) Tb response to CHA (0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle in C57BL/6J (WT) and Adora1−/− (KO) mice. (H,I) Tb response to CHA (0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle in C57BL/6J (WT) and Adora3−/− (KO) mice. (J,K) Tb response to CHA (0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle in C57BL/6J (WT) and Adora1−/−;Adora3−/− (DKO) mice. In F–K, data are mean ± SEM, n=5–10/group in a crossover design; every tenth SEM is shown in F, H, and J; * p<0.05, *** p<0.001.