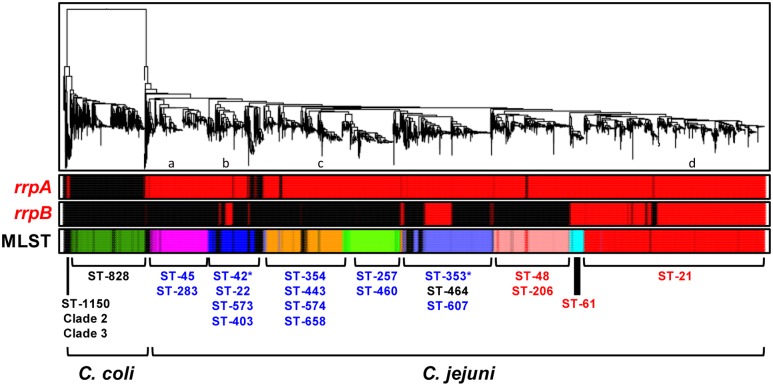
FIGURE 1.
Prevalence of the rrpA and rrpB genes among 3,746 Campylobacter jejuni and 486 C. coli genomes. Genomes were phylogenetically clustered using FFPry feature frequency profiling with L = 18 (Van Vliet and Kusters, 2015). The first two rows labeled ‘rrpA’ and ‘rrpB’ indicate genomes possessing the respective genes, which are shown in red, while those lacking the pathway are shown in black. The third bar shows the primary combinations of MLST clonal complexes for C. jejuni and C. coli, with red-labeled clonal complexes representing livestock-associated lineages, blue-labeled clonal complexes representing water and wildlife-associated lineages (Stabler et al., 2013), with the exception of the ST-61 clonal complex, which has been described as cattle (livestock)-associated (Kwan et al., 2008; Rotariu et al., 2009). The asterisks at ST-42 and ST-353 indicate that these clonal complexes may have a proportion of livestock-associated isolates. The association of some clonal complexes such as ST-464 was not reported previously and these are in black font. The lowercase letters indicate the approximate position of reference strains 81116 and M1 (a), 81-176 (b), RM1221 (c) and NCTC 11168 (d).