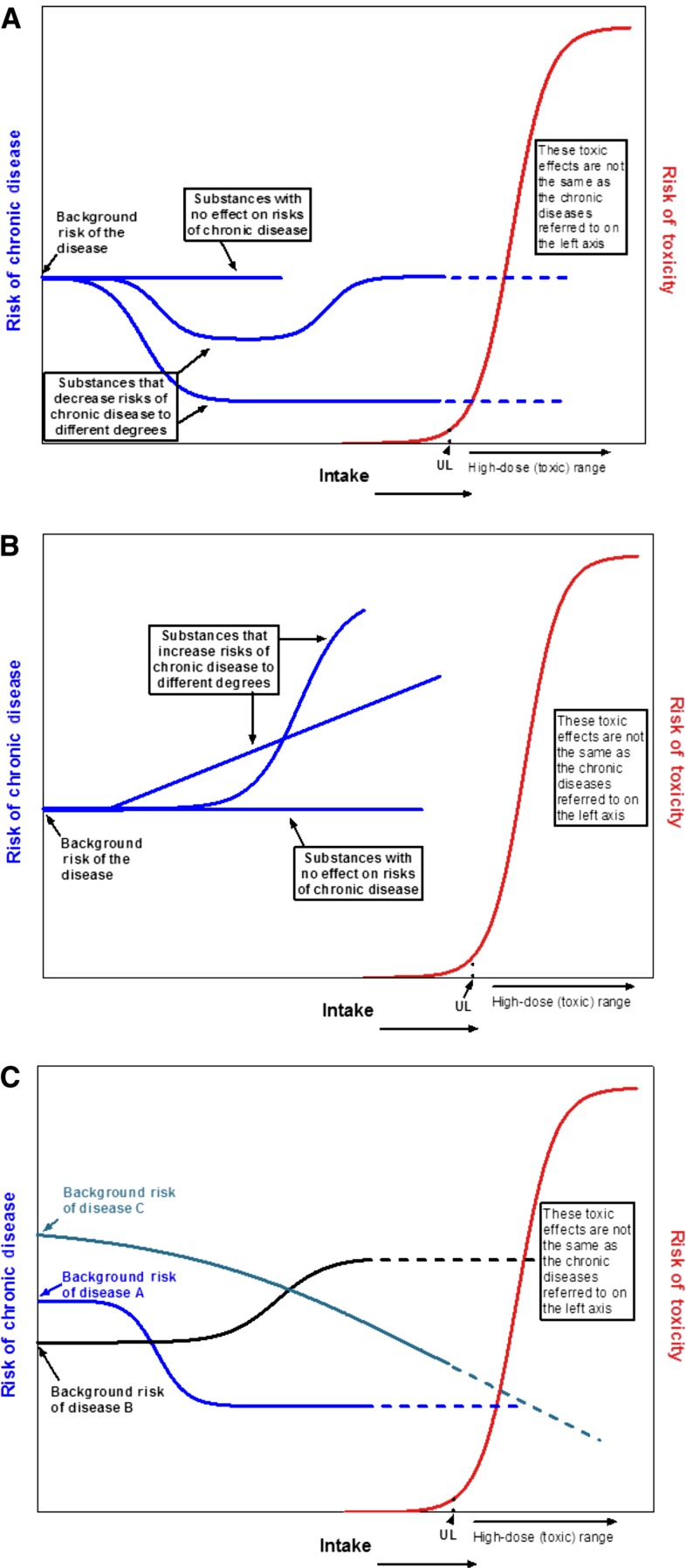
FIGURE 5.
Intake-response relations between the intake of a food substance and chronic disease risks can vary. The intake of a food substance could decrease (A) or increase (B) chronic disease risk. The intake of a food substance could be independently related to multiple chronic diseases that show different and overlapping dose-response relations (C). The relation or relations between the intake of the food substance and chronic disease or diseases might not be monotonic. The background risk of a given chronic disease is not zero. “Substances” could be individual food substances or groups of interacting substances. UL, Tolerable Upper Intake Level.