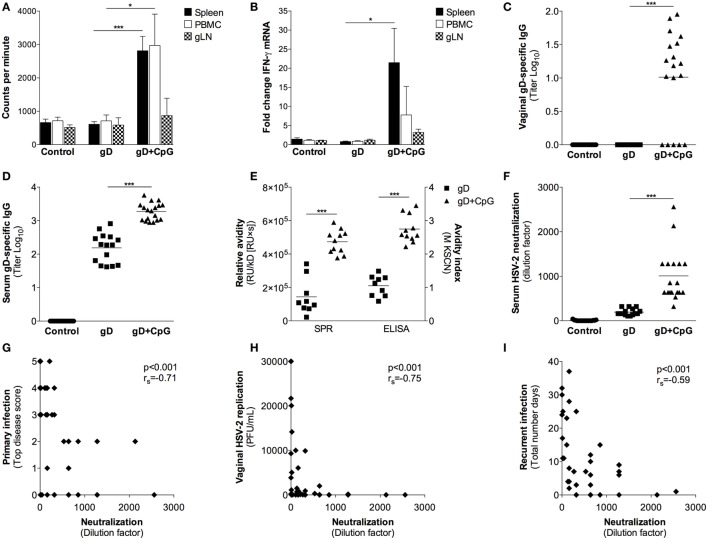
Figure 2.
Characterization of immune responses elicited after nasal immunization in guinea pigs. Guinea pigs were immunized as explained in Figure 1. Four weeks after the final immunization cells isolated from spleen, blood, and genital lymph nodes (gLN) were re-stimulated with gD protein in vitro. (A) After 72 h, splenocytes, PBMC and gLN cells (n = 4) were harvested and proliferation recorded as counts per minutes. (B) The RNA samples obtained from the cultured cells at 24 (gLN) and 48 h (spleen and PBMC) were analyzed for IFN-γ mRNA levels by real-time PCR. Results show IFN-γ expression in gD-stimulated cells expressed as fold change over unstimulated cells. (C,D) The content of gD-specific IgG in sera and vaginal swabs taken 4 weeks after the last immunization was determined by a gD-specific ELISA (n = 15–18). Results are expressed as titer (Log10), based on the mean optical density (OD) value at 490 nm with a threshold of 0.4 above the background OD. (E) HSV-2 neutralization effect of sera was examined by a HSV-2 neutralization assay on monolayers of GMK-AH1 cells. The neutralizing properties of sera are presented as the highest dilution factor resulting in 50% reduction of the cytopathic effect. (F) Avidity of gD-specific IgG in sera measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and KSCN based ELISA. SPR data presented as avidity score (response unit (RU)/dissociation rate constant (kD)[RU × s]) and ELISA data as avidity index. Serum neutralization capacity plotted against (G) primary disease score (top score), (H) vaginal HSV-2 replication at day 3 post-challenge and (I) the number of recurrent days. The Spearman correlation coefficient is indicated in each plot. Data in (A,B) are expressed as the mean + SEM. Individual guinea pig data in (C–I) are represented by each dot and the lines in (C–F) indicate the mean value for each individual group. Results shown in (A,B) are pooled from two independent experiments. Results shown in (C,F,I) are pooled from three independent experiments. Data in (A–E) were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison test (CI 95%), while the results in (F) were analyzed with a two-tailed unpaired t test and 95% CI. Differences were considered statistically significant at p values of <0.05 (*), <0.01 (**), and <0.001 (***).