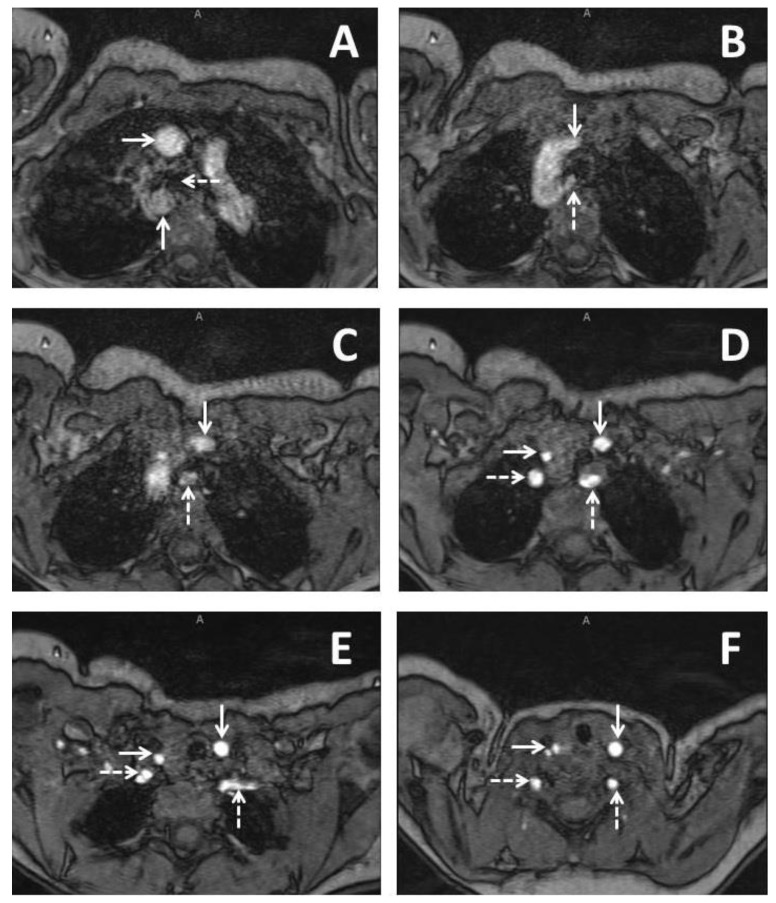
Figure 1.
Imaging from a three months old baby girl with DiGeorge syndrome who had some issues with feeding. Series of axial slices from magnetic resonance imaging presented in an inferior to superior progression. Panel A demonstrates a right sided aortic arch with the ascending aorta (solid horizontal arrow) coursing anterior to the right bronchus (dashed horizontal arrow) and the descending aorta (solid vertical arrow) coursing immediately posterior to the right bronchus; Panel B demonstrates the left common carotid (solid vertical arrow) as the first branching head and neck vessel and arises from the ascending aorta. An aberrant left subclavian artery (dashed vertical arrow) is seen as the last branching head and neck vessel and arises from the descending aorta; Panel C demonstrates the course of the left common carotid (solid vertical arrow) and aberrant left subclavian artery (dashed vertical arrow); Panel D demonstrates bifurcation of the brachiocephalic trunk into the right common carotid (solid horizontal arrow) and the right subclavian artery (dashed horizontal arrow). The left common carotid (solid vertical arrow) and the left subclavian artery (dashed vertical arrow) are seen demonstrated as well; Panel E demonstrates the right vertebral artery arising from the right subclavian artery (dashed horizontal arrow). The right common carotid (solid horizontal line), left common carotid (solid vertical arrow, and aberrant left subclavian (dashed vertical arrow) are also demonstrated; Panel F demonstrates early bifurcation of the right common carotid into the right internal and external carotid arteries (solid horizontal arrow). The right vertebral artery (dashed horizontal arrow), the left common carotid (solid vertical arrow), and the left vertebral artery are also demonstrated (dashed vertical arrow).