Fig. 4.
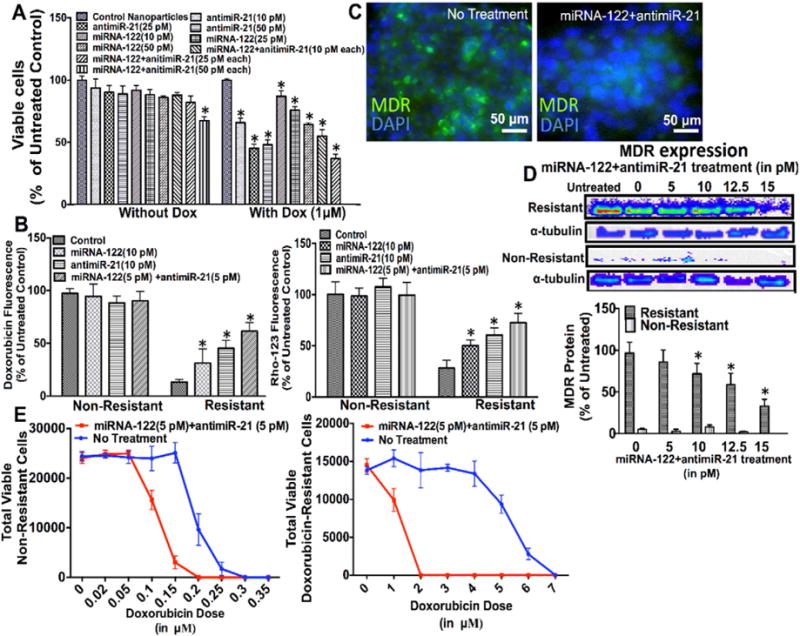
(A) Cell proliferation assay of HCC cells with strong doxorubicin resistance (5 μM) treated with different doses of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 (10, 25, 50 picomoles), either individually or in combination, shows that the miRNA combination therapy resulted in the strongest inhibition of cell proliferation. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 6 each. When HCC cells were treated with the miRNA combination treatment and doxorubicin, all cells died at a miRNA dose of 50 picomoles each. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 6 each. α tubulin was used as loading control. (B) Treatment with the miRNA combination therapy increased both doxorubicin and Rho-123 uptake in resistant HCC cells, suggesting decreased multi drug resistance (MDR) protein expression following miRNA treatment. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 12 each. This was confirmed by fluorescence imaging (C), and western blotting (D) showing decreased MDR protein expression in doxorubicin resistant HCC cells after treatment with the miRNA combination therapy. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 3 each. α tubulin was used as loading control. (E) Cell viability of non-resistant (left) and doxorubicin resistant (right) HCC cells treated with the miRNA combination therapy for 18 h followed by increasing doxorubicin doses shows increased therapeutic effects of doxorubicin in both cell types; n = 6 each.
