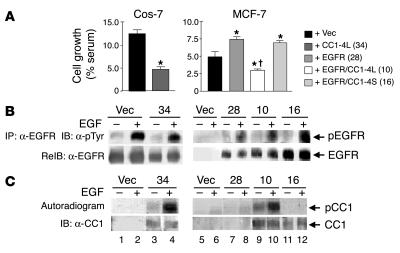
Figure 5.
CEACAM1-4L downregulates cell growth in response to EGF. (A) Cos-7 and MCF-7 cells were stably transfected with vector alone (+ Vec) or with cDNA encoding rat CEACAM1-4L (+ CC1-4L), EGFR (+ EGFR), or both (+ EGFR/CC1-4L). Cells were also transfected with cDNA encoding EGFR and CEACAM1_4S (+ EGFR/CC1-4S). Numbers in parentheses (in key) denote the clone number. After being incubated for 24 hours in serum-containing complete medium (maximal growth) or in serum-free medium supplemented with 0.1% BSA either alone (basal growth) or with 100 nM EGF, cells were counted by the MTT method. EGF-induced cell growth was calculated as the percent maximal minus basal growth divided by the number of cells grown in complete medium. These experiments were performed in triplicate and were repeated at least three times per clone. Data represent the mean ± SD of repeated experiments. At least two stable clones were examined. *P < 0.05 versus Vec; P < 0.05 versus EGFR (clone 28). (B) For examination of EGFR phosphorylation, serum-starved cells were treated with EGF as described in Figure 1 and lysed and the EGFR immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, immunoblotting with α-pTyr for detection of tyrosine-phosphorylated EGFR, and re-immunoblotting with α-EGFR to account for the amount of EGFR in the immunoprecipitates. (C) For examination of CEACAM1-4L phosphorylation, cell lysates were lectin-purified prior to phosphorylation in the presence of EGF and [γ-32P]ATP, immunoprecipitation of CEACAM1-4L, and analysis of its phosphorylation by autoradiography (upper gel). To account for the amount of CEACAM1-4L in the immunoprecipitate, proteins were reprobed with α-CC1 (lower gel).