Scheme 1.
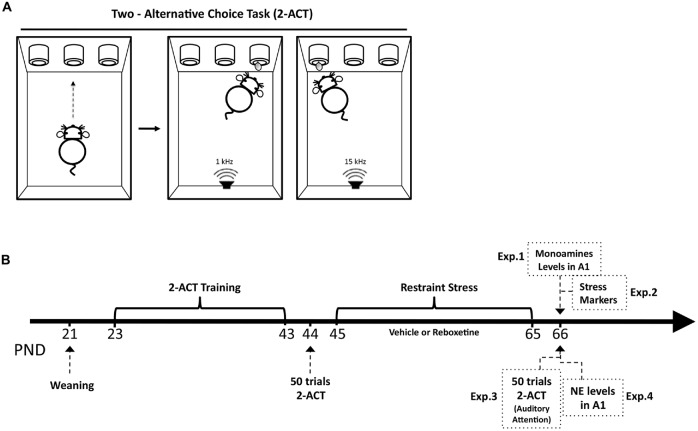
Structure of the basic two-alternative choice task (2-ACT) and schematic drawing of the experimental design. (A) 2-ACT is an auditory attention task; the trial initiates when the rat pokes its nose into the center port (left), which triggers the computer to randomly present one of two types of auditory stimuli, a high (15 kHz) or low (1 kHz) frequency tone (right). Rats were trained to respond with a left poke for high tones and a right poke for low tones; correct trials were rewarded with water. (B) The arrow represents the postnatal days of the animals (PND). After weaning, rats were trained in the 2-ACT for 20 days. Afterward, animals were randomly assigned to two experimental groups: control and stress. Trained rats were used in the Experiment 1 (Exp. 1) to determine monoamine levels in A1 1 day after chronic stress ended, and in Experiment 2 (Exp. 2) to analyze the stress markers. Experiment 3 (Exp. 3) analyzed the effects of chronic stress on auditory attention. Trained rats that were subjected to 50 2-ACT trials 1 day before and after the restraint stress protocol. A difference score (DS) was then determined by subtracting the correct trials after chronic stress (DS-CT) from those before. Experiment 4 (Exp. 4) analyzed NE levels in rats treated with reboxetine.